In the context of globalization, the supply chains are lengthening and involving many partners, multiple geographical areas, and many products. These networks pose inherent advantages such as cost reduction and globalization, but on the other side, they are a key cybersecurity threat. Any intervention in the supply chain can provoke spiralling consequences, lead to different economic losses, jeopardise an organization’s reputation, and, in a worst-case scenario, endanger society’s security on a national level.
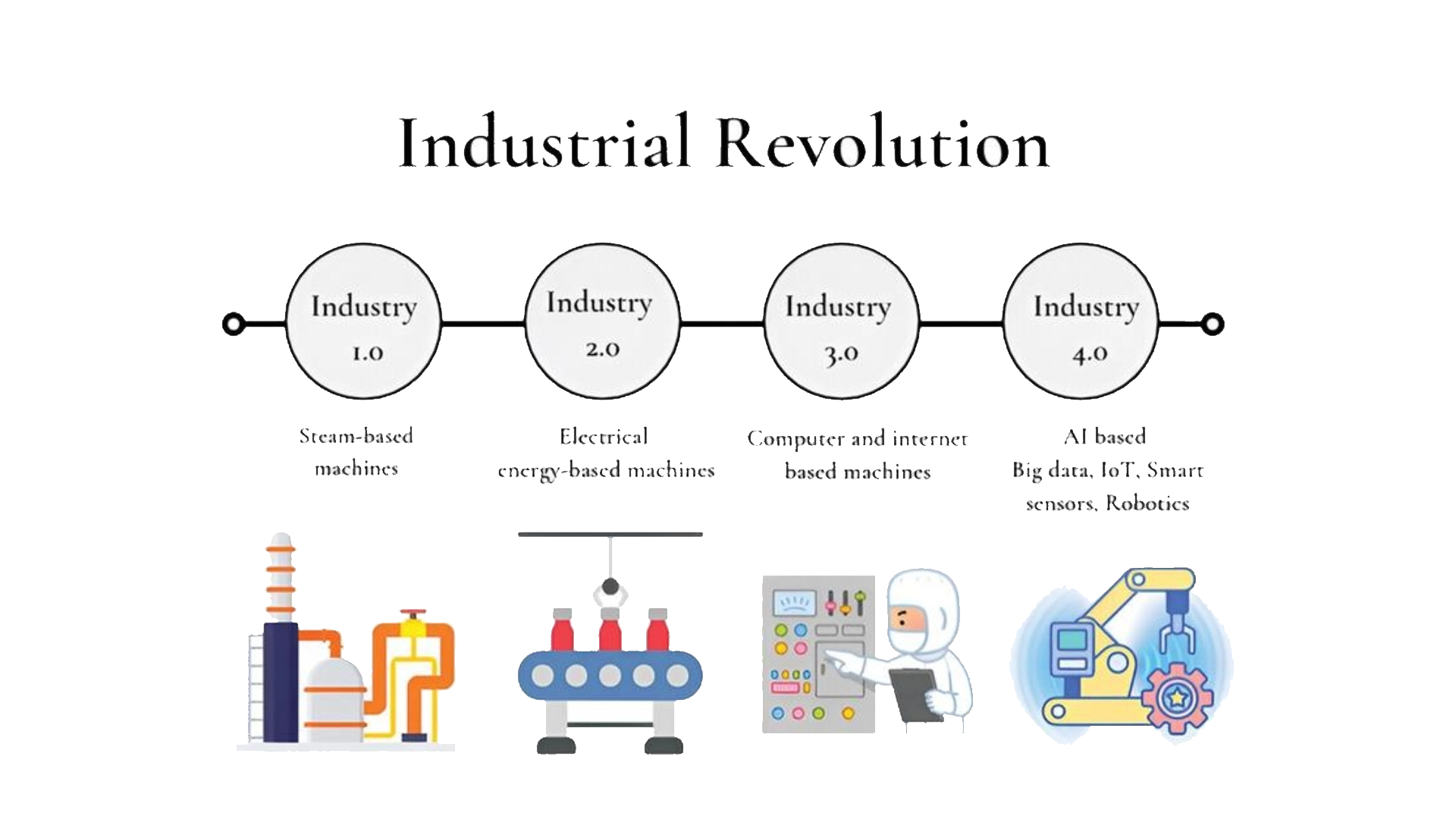
Modern threats such as cyber threats to the supply chain, third-party risks, ransomware attacks on suppliers and data breaches have made organizations change their perspective. While threats change, attempted security measures are insufficient in many cases. That is where Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) can be useful. By deploying the foregoing advanced technologies, risks associated with the supply chain can be detected, prevented, and minimized.
In this blog, the author plans to cover how AI and ML make the supply chain more secure and the advantages, limitations, and use cases of these technologies.
An analysis of the concepts of AI & ML in supply chain security
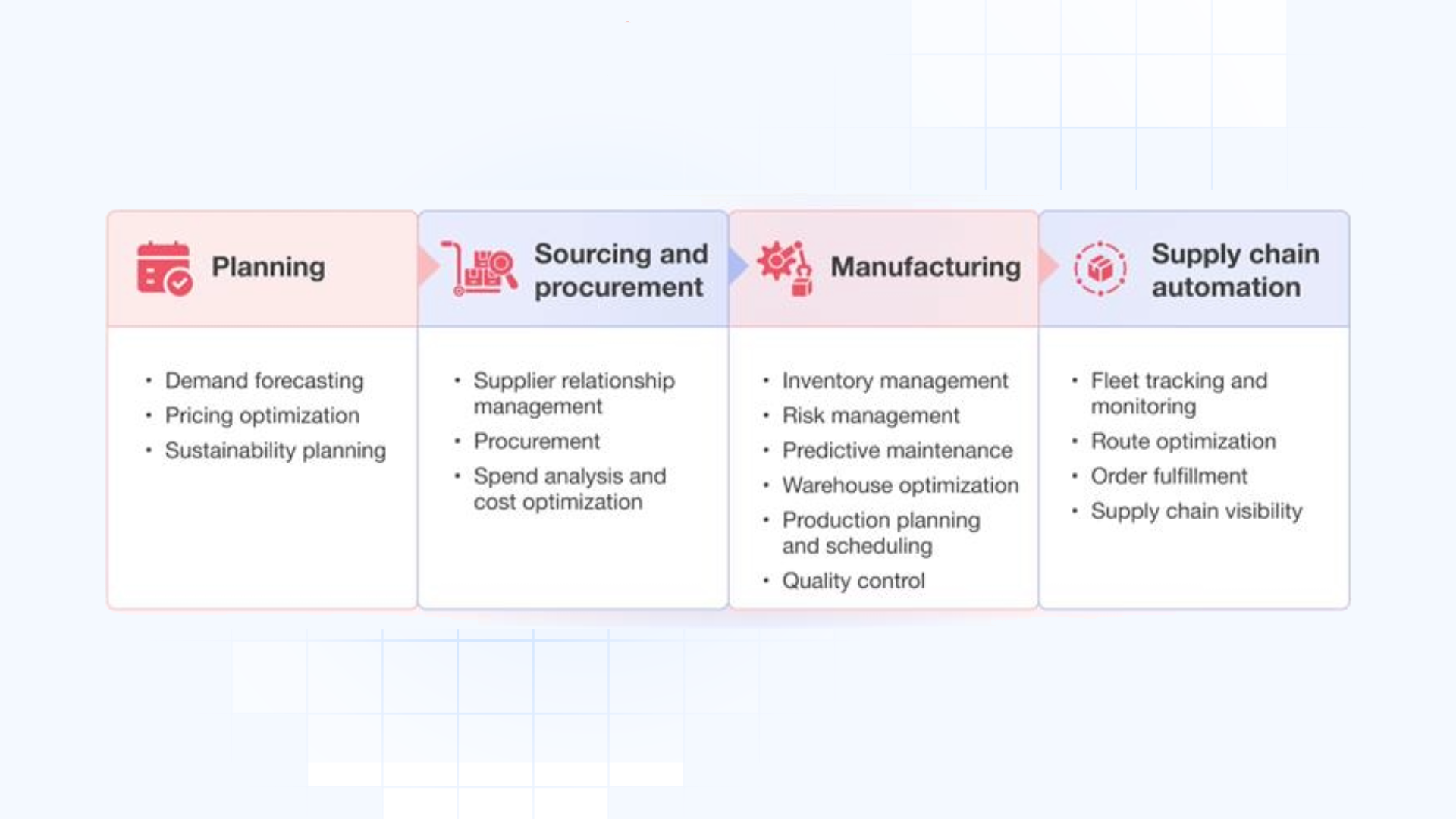
Before diving into their applications, it’s essential to understand the difference between AI and ML:
- AI: In its broader sense, AI is defined as machines capable of performing cognitive tasks that a human would, including, but not limited to, learning and reasoning.
- ML: It is that part of AI that deals with algorithms to learn and improve from data, having the capacity to learn and decide after being trained to do so.
In supply chain security, AI and ML are applied to detect threats, process big data, forecast threats, and react to threats in real-time. For instance, by analyzing large quantities of the data produced by the supply chain, from IoT sensors to transactional systems or third parties, such technologies can help businesses identify patterns and potential security threats more efficiently than other approaches.
Use of AI and ML in Supply Chain Security

Threat Identification and Outsourcing of Anomalies
AI and Machine learning can analyze vast amounts of data gathered from the entire supply chain to look for the emergence of any threat pattern in real-time. These systems are capable of detecting anomalies in behaviour, such as:
- Unexpected Supplier Activity: Using Big Data, ML models can detect fraud and cyberattacks in interactions with suppliers that could previously be masked, for example, sharp increases in order volume or changes in delivery times.
- Unusual Network Traffic: AI mechanisms can monitor specific network movements in an organization to detect hacking, unauthorized access, or data leakage. These are early indications of cyber activities affecting the supply chain.
- Credential Compromise: By implementing ML, a company can analyze access logs to help identify attempts of unauthorized access to systems or even information made by third-party vendors.
Risk Evaluation for forecast and protection
Predicting security risks is key to using AI and ML for supply chain security. Machine learning models leverage past data to predict future supply chain disruptions, allowing businesses to mitigate risks. These technologies can predict:
- Potential Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities: It allows using ML to detect vulnerabilities in the digital supply chain, in other words, to search for weak points that cybercriminals can target.
- Natural Disasters and Disruptions: Based on data on weather and geopolitical conditions and past occurrences, AI systems can anticipate disruptions in the supply chain caused by external factors, including floods, earthquakes, or political instabilities, and hence prepare the firms for such changes.
- Supplier Risks: Predictive algorithms can determine risks within a business supplier chain using suppliers’ performance data, financial status, and compliance with security regulations.
Automated Response and Remediation
AI and ML enable automatic responses to any detected threats or vulnerabilities. Once an attack or breach has occurred, AI-driven systems can rapidly respond to mitigate the threat, cause as little damage as possible, and minimize manual intervention. Some examples of automated responses include:
- Containment of Threat: If suspicious traffic is seen through an AI system in a supplier’s network, the system automatically sends a signal to isolate itself, thus preventing malware and ransomware from spreading.
- Smart Contract Execution: Blockchain technology and AI can be integrated to create smart contracts that automatically enforce the desired security measures. Smart contracts shall provide mechanisms for ensuring that participants in the supply chain comply with the security requirements agreed upon beforehand.
- Automation of Incident Response: Specific conditions could be fed into an ML model so that when any of these conditions are sensed, suitable incident response activities will be triggered automatically; these can include blocking malicious IP addresses, encrypting data at once when a cyber-attack has been detected, or sending alerts to affected stakeholders.
Visibility and Traceability within the Supply Chain
AI and ML technologies improve the transparency of supply chains since they can trace a product from the origin point to the final delivery point. This will enhance the security of supply chains by identifying the source of potential interruptions or threats against such businesses and will ensure the integrity of their products. Some of the applications include:
- IoT Sensors and Edge Devices: An intelligent IoT device can give real-time information on where and how products are inside an organization. Thus, if such a breach occurred, they would indicate where and how a product was breached.
- Blockchain for Product Authentication: This will help authenticate the product so that no counterfeit products enter the supply chain. This is highly relevant to pharmaceuticals, electronics, and some other industries.
Advantages of AI and ML Supply Chain Security
Efficiency: AI and ML automate redundant tasks such as threat detection, data analysis, and reporting. These activities will significantly minimize the human security team’s workload. Automation ensures that increased response times are checked, making companies better prepared to respond to threats before they become large problems.
Accuracy is Enhanced: These AI-based models can deal with really big datasets with great precision. Unlike conventional security measures that depend on heuristic or rule-based approaches, AI and ML can learn and develop their threat detection capabilities over time by learning from new threats.
Cost Savings: It supports businesses in reducing manual interferences, further decreasing the related cost of their security. Due to its predictability, it may prevent companies from a cost-loss supply chain delay and downtime.
Scalable Security: The AI and ML systems can scale with the growth of the supply chain to provide security coverage as businesses expand into new regions or onboard additional suppliers. As the prompt illustrates, that’s crucial for this long and interlinked supply chain.
Limitations and Challenges in Supply Chain Security AI and ML
- Quality and availability of data: High-quality data is imperative for AI and ML applications. Poor quality or incomplete data will likely result in poor predictions and inefficient security controls. Organizations must invest significantly in data collection, cleaning, and integration to make AI and ML applications effective.
- Complexity of implementation: Integrating AI and ML technologies into existing supply chain systems is often capital-intensive and requires a one-time upfront investment. To develop, deploy, and maintain such systems, enterprises require highly skilled professionals who understand cybersecurity and machine learning.
- Privacy Issues: Privacy issues become more prominent with more sensitive data processed through AI-powered solutions. There is also a much stricter need to ensure that companies comply with data protection regulations such as GDPR while implementing AI-based security solutions.
- Adversarial Attacks: Their AI and ML systems can be subject to adversarial attacks, where malicious parties change the model’s inputs to prevent detection. While AI can recognize known threats, new and more difficult attacks may outsmart such systems unless their constant updates are in play.
AI and ML in Supply Chain Security: Real-world Applications
- Maersk Cyber Attack and Introduction to AI: In 2017, another huge shipping company was victim to a massive cyber-attack, which brought the company’s whole global operation down. In that scenario, Maersk adopted AI and ML as part of its security plan, which has helped the company manage risk efficiently and proactively. It now monitors abnormal behaviour through AI systems, thus avoiding further attacks.
- Walmart and Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics by Walmart identifies risks in the supply chain and makes products available on time in the markets. AI-based systems and their models based on historical data forecasted possible interruptions, thus giving advance notice to the company regarding which will be provided to Walmart so that it could assess and upgrade the security of activities in the supply chain.
- IBM’s Watson for Cyber Security: IBM’s Watson brings AI and ML into global companies’ supply chain security, helping them reduce business risk. Watson can process enormous amounts of data from different sources, ensuring organizations can discover and act on emerging threats in real-time, thus giving more potent security to global supply chains.
AI and ML are revolutionizing supply chain security as they can detect the most serious threats and manage risks more effectively and automatically than any earlier incident response system. Businesses can outstrip evolving cyber threats, increase efficiency, and reduce costs. Still, its successful implementation remains bound upon the quality of data available, skilled professionals, and constant monitoring of emerging risks. With increasingly complex and digitally interconnected supply chains, AI and ML will be critical in protecting them against cyber threats. Using these technologies, businesses can develop resilient, secure supply chains that can survive disruptions, mitigate risks, and protect invaluable assets.



