What is an Artificial Neural Network?
These are computational models inspired by the human brain. Many of the recent advancements have been made in the field of Artificial intelligence, including Voice Recognition, Image recognition, and Robotics using it. They are the biologically inspired simulations performed on the computer to perform certain specific tasks like
- Classification
- Pattern Recognition
Generally, it is a biologically inspired network of artificial neurons configured to perform specific tasks. These biological computing methods are the next major advancement in the Computing Industry.
What is a Neural Network?
‘Neural’ originates in the human (animal) nervous system’s basic functional unit, ‘neuron’ or nerve cells in the brain and other parts of the human (animal) body. A neural network is a group of algorithms that certify the underlying relationship in a set of data similar to the human brain. The neural network helps to change the input so that the network gives the best result without redesigning the output procedure. You can also learn more about ONNX in this insight.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ANN
The advantages are listed below
- A neural network can perform tasks that a linear program can not.
- When an element of the neural network fails, its parallel nature can continue without any problem.
- A neural network learns, and reprogramming is not necessary.
- It can be implemented in any application.
- It can be performed without any problem.
The disadvantages are described below
- The neural network needs training to operate.
- A neural network is different from the architecture of microprocessors. Therefore, emulation is necessary.
- Requires high processing time for large neural networks.
What are the parts of Neurons and their Functions?
The typical nerve cell of the human brain comprises four parts:
- Function of Dendrite: It receives signals from other neurons.
- Soma (cell body): It sums all the incoming signals to generate input.
- Axon Structure: When the sum reaches a threshold value, the neuron fires and the signal travels down the axon to the other neurons.
- Synapses Working: The point of interconnection of one neuron with other neurons. The amount of signal transmitted depends upon the strength (synaptic weights) of the connections.
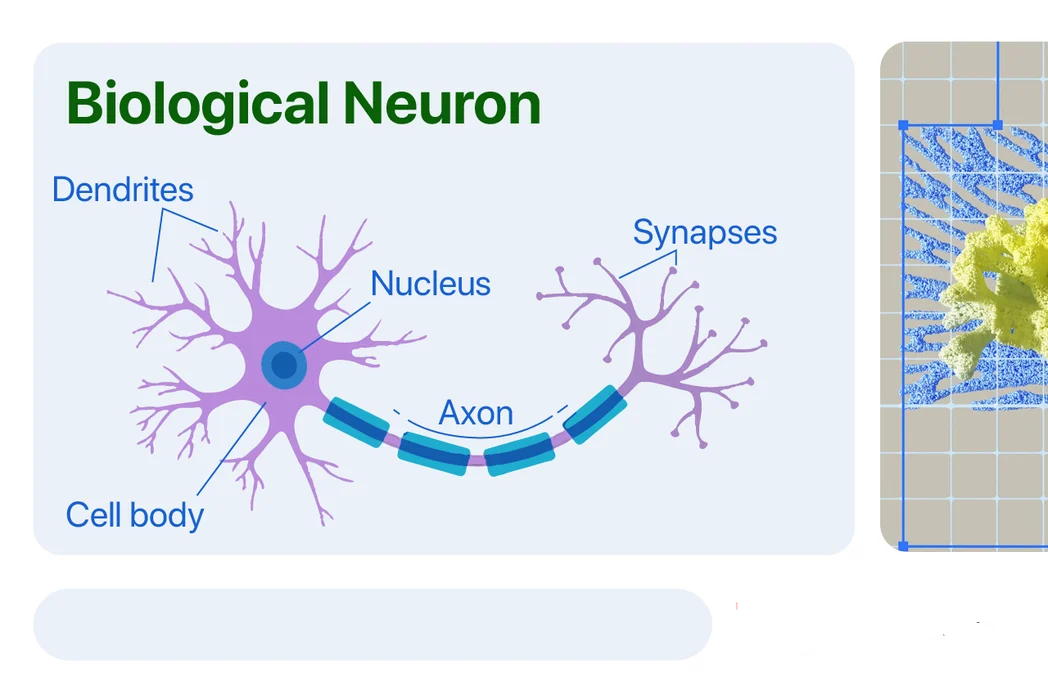
The connections can be inhibitory (decreasing strength) or excitatory (increasing strength) in nature. So, a neural network, in general, has a connected network of billions of neurons with a trillion of interconnections between them.
Differences Between Brain and Computer
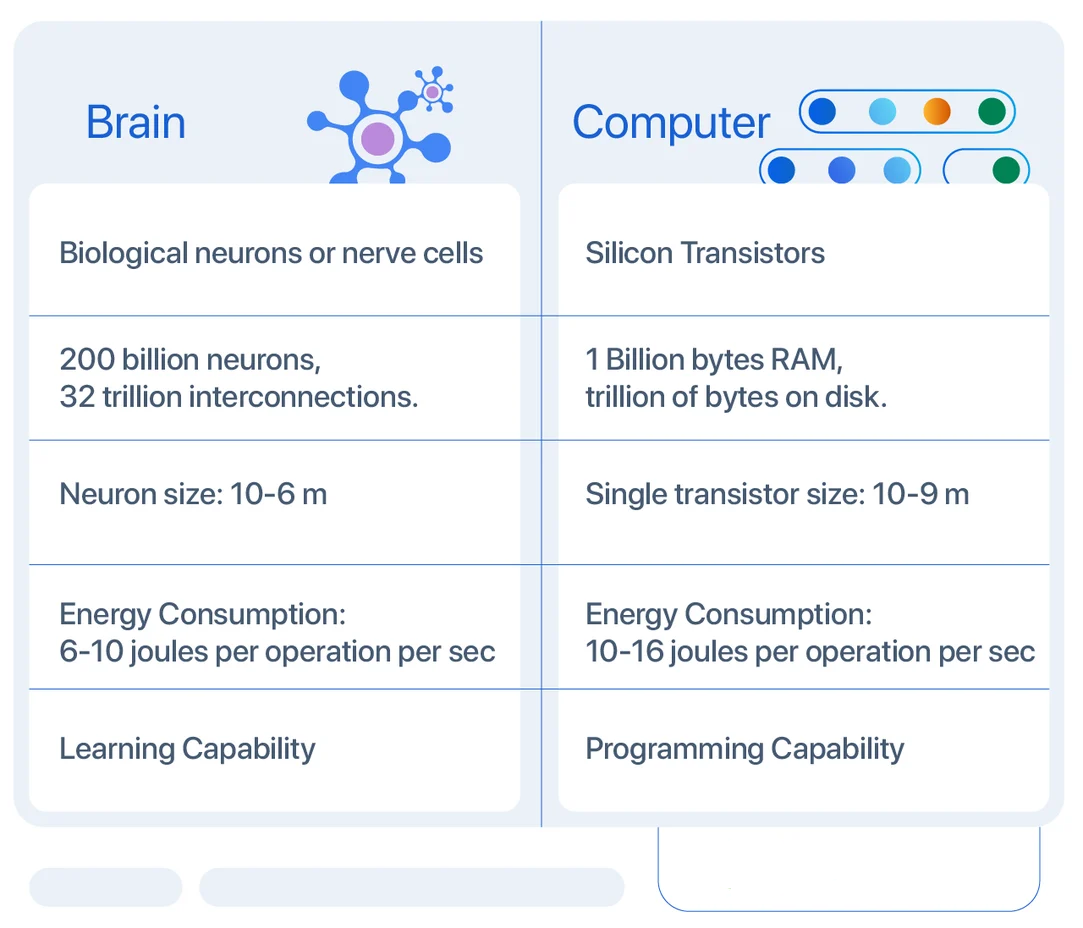
ANN vs. BNN: Key Distinctions
| Characteristics | Artificial Neural Network (ANN) | Biological (Real) Neural Network (BNN) |
| Speed | Faster in processing information. Response time is in nanoseconds. | Slower in processing information. The response time is in milliseconds. |
| Processing | Serial processing. | Massively parallel processing. |
| Size & Complexity | Less size & complexity. It does not perform complex pattern recognition tasks. | A highly complex and dense network of interconnected neurons containing neurons of the order of 1011 with 1015 of interconnections. |
| Storage | Information storage is replaceable means replacing new data with an old one. | A highly complex and dense network of interconnected neurons containing neurons of the order of 1011 with 1015 of interconnections. |
| Fault tolerance | Fault intolerant. Corrupt information cannot be retrieved in case of system failure. | Information storage is adaptable means new information is added by adjusting the interconnection strengths without destroying old information. |
| Control Mechanism | There is a control unit for controlling computing activities | No specific control mechanism external to the computing task |
Relationship Between ANN and BNN
Neural Networks resemble the human brain in the following two ways –
- A neural network acquires knowledge through learning.
- A neural network’s knowledge is stored within inter-neuron connection strengths known as synaptic weights.
| Von Neumann architecture-based computing | Ann-Based Computing |
| Serial processing: processing instruction and problem rule one at a time (sequential) | Parallel processing – several processors perform simultaneously (multitasking) |
| Function logically with a set of if & else rules – rule-based approach | Function by learning patterns from a given input (image, text video, etc.) |
| Programmable by higher-level languages such as C, Java, C++, etc. | ANN is, in essence, the program itself. |
| Requires either big or error-prone parallel processors | Use of application-specific multi-chips. |
Artificial Neural Network (ANN) vs. biological Neural Network (BNN)
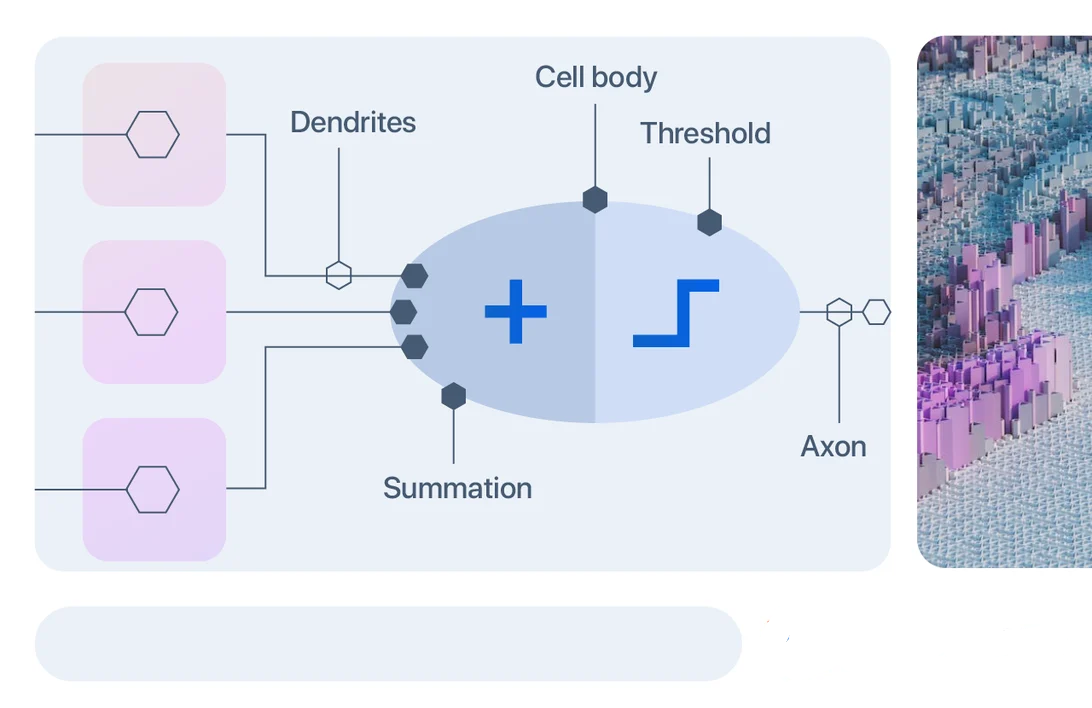
- The Biological Neural Network’s dendrites are analogous to the weighted inputs based on their synaptic interconnection in it.
- The cell body is comparable to the artificial neuron unit in it, comprising summation and threshold unit.
- An axon carries output analogous to the output unit. So, it is modeled using the workings of basic biological neurons.
How does ANN work?
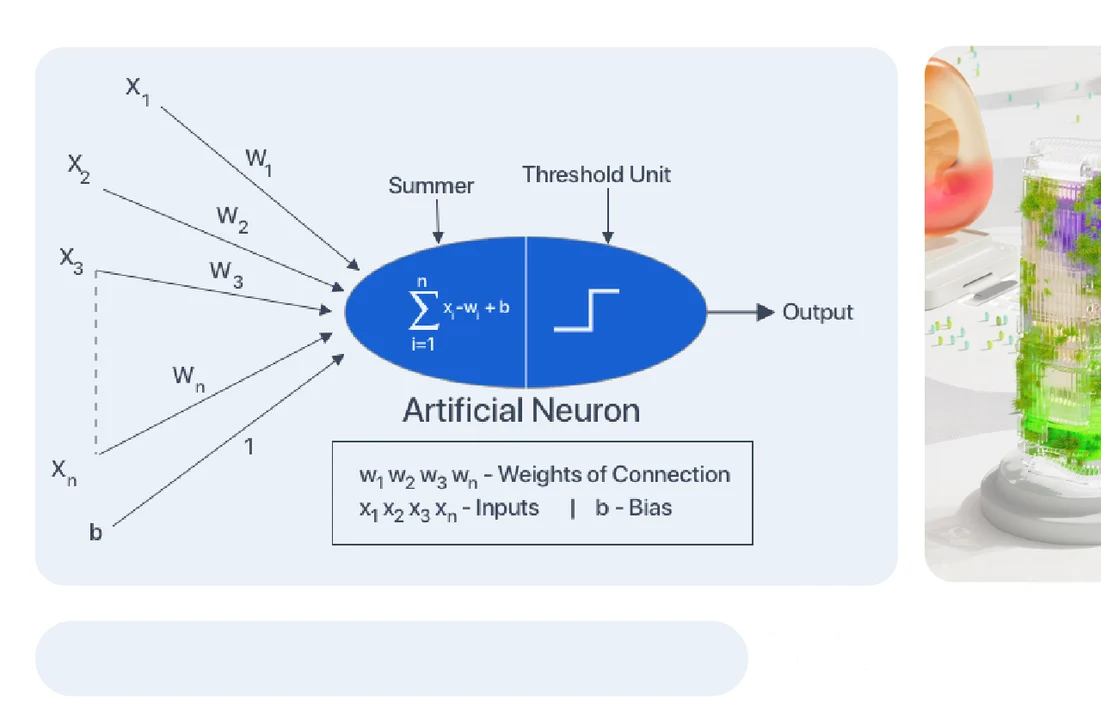
- It can be viewed as weighted directed graphs in which artificial neurons are nodes and directed edges with weights are connections between neuron outputs and inputs.
- The Artificial Neural Network receives information from the external world in patterns and images in vector form. These inputs are designated by the notation x(n) for n number of inputs.
- Every input is multiplied by its specific weights, which serve as crucial information for the neural network to solve problems. These weights represent the strength of the connections between neurons within the neural network.
- The weighted inputs are all summed up inside the computing unit (artificial neuron). If the weighted sum is zero, bias is added to make the output not zero or to scale up the system response. Bias has the weight and input always equal to ‘1′.
- The sum corresponds to any numerical value ranging from 0 to infinity. A threshold value is set up to limit the response to arrive at the desired value. For this, the sum is forwarded through an activation function.
- The activation function is set to the transfer function to get the desired output. There is a linear and a nonlinear activation function.
What are the commonly used activation functions?
Some of the commonly used activation functions are binary, sigmoidal (linear), and tan hyperbolic sigmoidal functions(nonlinear).
- Binary – The output has only two values, either 0 or 1. For this, the threshold value is set up. If the net weighted input is greater than 1, the output is assumed as one; otherwise, it is zero.
- Sigmoidal Hyperbolic – This function has an ‘S’ shaped curve. Here, the tan hyperbolic function is used to approximate the output of the net input. The function is defined as – f (x) = (1/1+ exp(-????x)) where ???? – steepness parameter.
Types of Neural Networks
| Parameter | Types | Description |
| Based on the connection pattern | FeedForward, Recurrent | Feedforward – In which graphs have no loops. Recurrent – Loops occur because of feedback. |
| Based on the number of hidden layers | Single-layer, Multi-Layer | Single Layer – Having one secret layer. E.g., Single Perceptron Multilayer – Having multiple secret layers. Multilayer Perceptron |
| Based on the nature of weights | Fixed, Adaptive | Fixed – Weights are a fixed priority and not changed at all. Adaptive – Updates the weights and changes during training. |
| Based on the Memory unit | Static, Dynamic | Static – Memoryless unit. The current output depends on the current input. E.g., Feedforward network. Dynamic – Memory unit – The output depends upon the current input as well as the current output. E.g., Recurrent Neural Network |
Neural Network Architecture Types
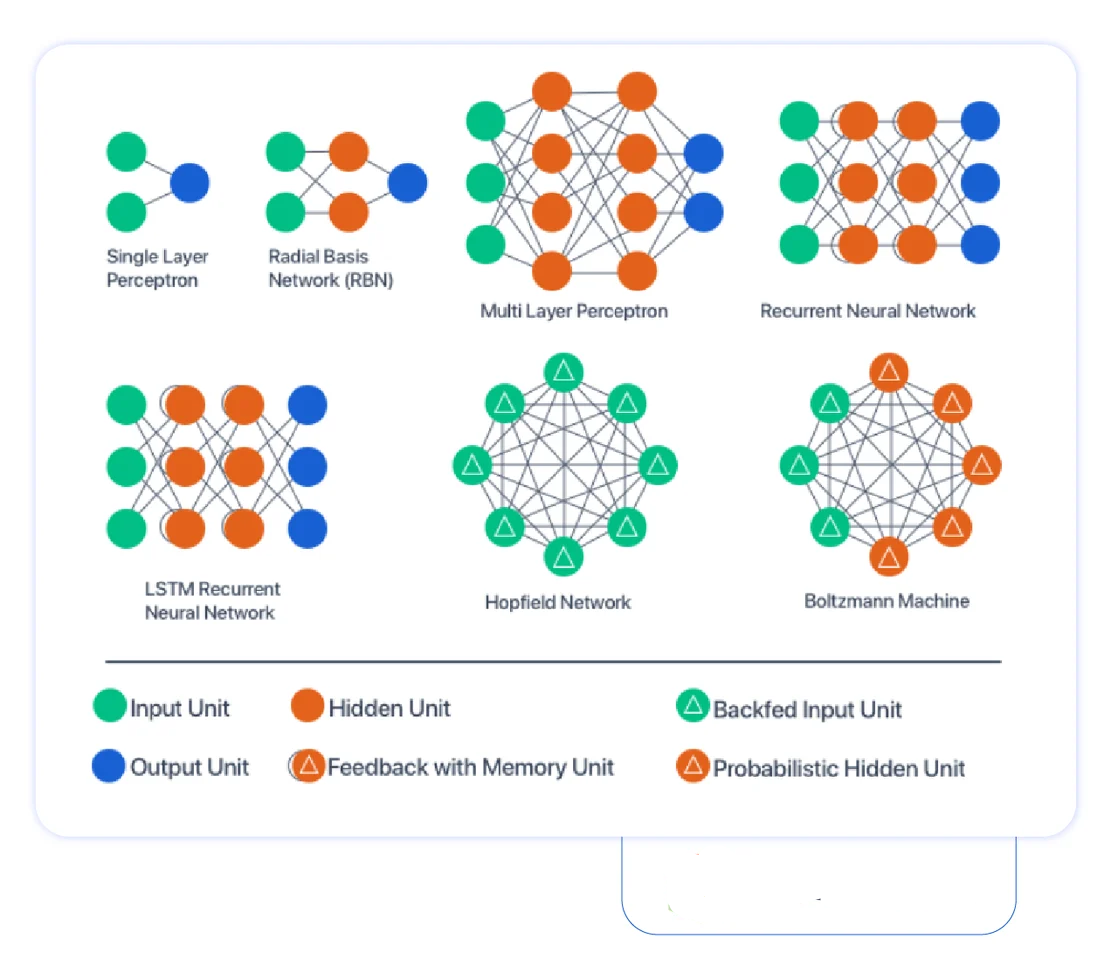
- Perceptron Model: A Neural Network has two input and one output unit with no hidden layers. These are also known as ‘single-layer perceptrons’.
- Radial Basis Function: These networks are similar to the feed-forward Neural Network, except the radial basis function is used as these neurons’ activation function.
- Multilayer Perceptron: Unlike single-layer perceptrons, deep feedforward neural networks use more than one hidden layer of neurons.
- Recurrent: Type of Neural Network in which hidden layer neurons have self-connections. It possesses memory. At any instance, the hidden layer neuron receives activation from the lower layer and its previous activation value.
- Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network (LSTM): An LSTM network is a type of neural network in which memory cells are incorporated into hidden-layer neurons.
- Hopfield Network: A fully interconnected network of neurons in which each neuron is connected to every other neuron. The network is trained with input patterns by setting a value of neurons to the desired pattern. Then, its weights are computed. The weights are not changed. Once trained for one or more patterns, the network will converge to the learned patterns. It is different from other Neural Networks.
- Boltzmann Machine Neural Network: These networks are similar to the Hopfield network, except some neurons are input, while others are hidden in nature. The weights are initialized randomly and learned through the backpropagation algorithm.
- Convolutional Neural Network: Get a complete overview of it through our blog Log Analytics with Machine Learning and Deep Learning.
- Modular Neural Network: It is the combined structure of different types of it like multilayer perceptron, Hopfield Networks, Recurrent Neural Networks, etc., which are incorporated as a single module into the network to perform independent subtasks of whole complete.
- Physical Neural Network: In this type of Artificial Neural Network, electrically adjustable resistance material is used to emulate synapses instead of software simulations performed in the neural network.
Hardware Architecture for Neural Networks
Two types of methods are used to implement hardware for it.
- Software simulation in conventional computer
- A special hardware solution for decreasing execution time
When neural networks are used with fewer processing units and weights, software simulation is performed directly on the computer, e.g., voice recognition. When Neural Network Algorithms develop to the point where useful things can be done with thousands of neurons and tens of thousands of synapses, high-performance Neural network hardware will become essential for practical operation.
E.g., GPU (Graphical processing unit) in the case of Deep Learning algorithms in object recognition, image classification, etc. The implementation’s performance is measured by connection per the second number (cps), i.e., the number of data chunks transported through the neural network’s edges. The performance of the learning algorithm is measured in the connection updates per second (cups).
Learning Techniques
The neural network learns by iteratively adjusting its weights and bias (threshold) to yield the desired output. These are also called free parameters. For learning to take place, the Neural Network must be trained first. The training is performed using a defined set of rules, the learning algorithm.
Training Algorithms
- Gradient Descent Algorithm: This is the simplest training algorithm used in a supervised training model. If the actual output is different from the target output, the difference or error is found. The gradient descent algorithm changes the network’s weights to minimize this mistake.
- Back Propagation Algorithm: It extends the gradient-based delta learning rule. Here, after finding an error (the difference between desired and target), the error is propagated backwards from the output layer to the input layer via the hidden layer. It is used in Multi-layer Neural Networks.
Learning Data Sets
- Training Data Set: A set of examples used for learning is to fit the parameters [i.e., weights] of the network. One approach comprises one full training cycle on the training set.
- Validation Set Approach: A set of examples used to tune the parameters [i.e., architecture] of the network. For example, to choose the number of hidden units in a Neural Network.
- Making Test Set: A set of examples is used only to assess the performance [generalization] of a fully specified network or apply successfully to predict output whose input is known.
Five Algorithms to Train a Neural Network
- Hebbian Learning Rule
- Self-Organizing Kohonen Rule
- Hopfield Network Law
- LMS algorithm (Least Mean Square)
- Competitive Learning
Architecture of Neural Networks
A typical Neural Network contains many artificial neurons called units arranged in layers. A typical Artificial Neural Network comprises different layers –
Input layer
- It contains those units (Artificial Neurons) that receive input from the outside world on which the network will learn, recognize, or otherwise process.
Output layer
- It contains units that respond to the information about how it learns any task.
Hidden layer
- These units are between the input and output layers. The hidden layer transforms the input into something the output unit can use.
- Connect Neural Networks, which means that each hidden neuron links completely to every neuron in its previous layer(input) and the next layer (output).
Learning Techniques
- Supervised Learning: In this learning, the training data is input to the network, and the desired output is known weights are adjusted until production yields the desired value.
- Unsupervised Learning: Use the input data to train the network whose output is known. The network classifies the input data and adjusts the weight by feature extraction in input data.
- Reinforcement Learning: Here, the output value is unknown, but the network provides feedback on whether the output is right or wrong. It is Semi-Supervised Learning.
- Offline Learning: The weight vector and threshold adjustments are made only after the training set is shown to the network. It is also called Batch Learning.
- Online Learning: The weight and threshold adjustments are made after presenting each training sample to the network.
Learning and Development
Learning occurs when the weights inside the network are updated after many iterations. For example, suppose we have inputs in the form of patterns for two different classes of patterns — I & 0, as shown, and b — bias and y, as the desired output.
We want to classify input patterns into either pattern ‘I’ & ‘O.’ The following are the steps performed:
- Nine inputs from x1 – x9 and bias b (input having weight value 1) are fed to the network for the first pattern.
- Initially, weights are initialized to zero.
- Then weights are updated for each neuron using the formulae: Δ wi = xi y for i = 1 to 9 (Hebb’s Rule)
- Finally, new weights are found using the formulas:
- wi(new) = wi(old) + Δwi
- Wi(new) = [111-11-1 1111]
- The second pattern is input to the network. This time, weights are not initialized to zero. The initial weights used here are obtained after presenting the first pattern. By doing so, the network.
- The steps from 1 – 4 are repeated for the second input.
- The new weights are Wi(new) = [0 0 0 -2 -2 -2 000]
So, these weights correspond to the learning ability of the network to classify the input patterns successfully.
Use Cases of ANN
There are four broad use cases of Neural Networks
Classification Neural Network: Using feedforward networks, a neural network can be trained to classify a given pattern or dataset into a predefined class.
Prediction Neural Network: A Neural Network can be trained to produce expected outputs from a given input, such as stock market predictions.
Clustering Neural Network: The neural network can identify a unique feature of the data and classify them into different categories without any prior knowledge of the data. The following networks are used for clustering
- Competitive networks
- Adaptive Resonance Theory Networks
- Kohonen Self-Organizing Maps.
- Association Neural Network
Train the Neural Network to remember the particular pattern. When the noise pattern is presented to the network, the network associates it with the memory’s closest one or discards it. For example, Hopfield Networks performs recognition, classification, clustering, etc.
Applications of Neural Networks
Top applications of neural networks:
- Neural Network for Machine Learning
- Face Recognition using it
- Neuro-Fuzzy Model and its Applications
- Neural Networks for data-intensive applications
Neural Networks for Pattern Recognition
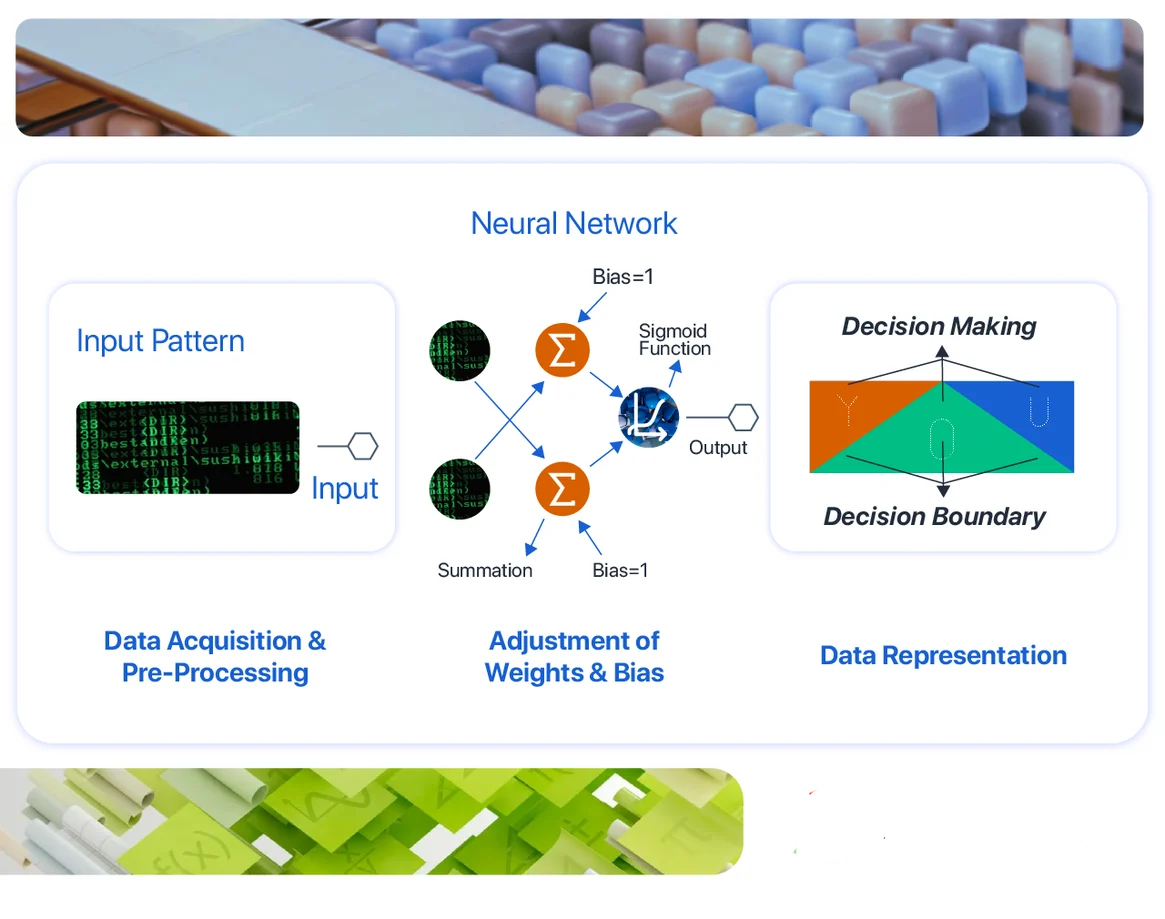
Pattern recognition studies how machines can observe the environment, learn to distinguish patterns of interest from their background and make sound and reasonable decisions about the patterns’ categories. Some examples of the pattern are – fingerprint images, a handwritten word, a human face, or a speech signal. Given an input pattern, its recognition involves the following task –
- Supervised classification – Given that the input pattern is known as the member of a predefined class,
- Unsupervised classification – Assign a pattern to a hitherto unknown class.
So, the recognition problem here is essentially a classification or categorized task. The design of pattern recognition systems usually involves the following three aspects-
- Data acquisition and preprocessing
- Data representation
- Decision Making
Approaches For Pattern Recognition
- Template Matching
- Statistical
- Syntactic Matching
Following Neural Network architectures used for Pattern Recognition –
- Multilayer Perceptron
- Kohonen SOM (Self-Organizing Map)
- Radial Basis Function Network (RBF)
Neuro-Fuzzy Model and its Applications
Fuzzy logic: Fuzzy logic refers to logic developed to express the degree of truthiness by assigning values between 0 and 1, unlike traditional boolean logic, which represents 0 and 1.
What is Fuzzy logic’s role in Neural networks: Fuzzy logic and it have one thing in common. They can be used to solve pattern recognition problems and others that do not involve any mathematical model.
What are the applications of the Neuro-Fuzzy Model: Systems combining both fuzzy logic and neural networks are neuro-fuzzy systems. These systems (Hybrid) can combine the advantages of both it and fuzzy logic to perform better. Fuzzy logic has been integrated for use in the following applications –
- Automotive engineering
- Applicant screening of jobs
- Control of the crane
- Monitoring of glaucoma
In a hybrid (neuro-fuzzy) model, Neural Networks Learning Algorithms are fused with the fuzzy reasoning of fuzzy logic. It determines the values of parameters, while if-then rules are controlled by fuzzy logic.
Neural Network for Machine Learning
- Multilayer Perceptron (supervised classification)
- Back Propagation Network (supervised classification)
- Hopfield Network (for pattern association)
- Deep Neural Networks (unsupervised clustering)
- Neural Networks for data-intensive applications
It has been successfully applied to the broad spectrum of data-intensive applications, such as:
| Application | Architecture / Algorithm | Activation Function |
| Process modeling and control | Radial Basis Network | Radial Basis |
| Machine Diagnostics | Multilayer Perceptron | Tan- Sigmoid Function |
| Portfolio Management | Classification Supervised Algorithm | Tan- Sigmoid Function |
| Target Recognition | Modular Neural Network | Tan- Sigmoid Function |
| Medical Diagnosis | Multilayer Perceptron | Tan- Sigmoid Function |
| Credit Rating | Logistic Discriminant Analysis with ANN, Support Vector Machine | Logistic function |
| Targeted Marketing | Back Propagation Algorithm | Logistic function |
| Voice recognition | Multilayer Perceptron, Deep Neural Networks( Convolutional Neural Networks) | Logistic function |
| Financial Forecasting | Backpropagation Algorithm | Logistic function |
| Intelligent searching | Deep Neural Network | Logistic function |
| Fraud detection | Gradient – Descent Algorithm and Least Mean Square (LMS) algorithm. | Logistic function |
What is the learning rule in neural networks?
The learning rule is a type of mathematical logic. It encourages to gain from the present conditions and upgrade its efficiency and performance. The brain’s learning procedure modifies its neural structure. The expanding or diminishing quality of its synaptic associations relies upon their activity. Learning rules in the Neural network:
- Hebbian learning rule: It determines how to customize the weights of a system’s nodes.
- Perceptron learning rule: The network starts learning by assigning a random value to each load.
- Delta learning rule: Modification in a node’s sympatric weight is equal to the multiplication of the error and the input.
- Correlation learning rule: It is similar to supervised learning.



