Global Generative AI trends
The generative AI market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by technological advancements and increasing demand across various sectors. Generative AI applications are transforming industries by enhancing user experiences, streamlining workflows, and providing valuable insights from complex datasets.
- Projected Market Growth: The generative AI market is projected to grow at 47.5% CAGR, increasing from $43.87 billion in 2023 to $667.96 billion by 2030.
- Enterprise Adoption Rate: By 2026, over 80% of enterprises are expected to adopt generative AI APIs or models, up from under 5% in 2023.
Unlike analytical and traditional AI-based conversational interfaces constrained by pre-defined commands, conversational AI comprehends, learns, and crafts chat responses based on context and intent. Generative virtual assistants, leveraging models like NLP, deep learning, and NLG, empower conversational interfaces to engage users in human-like interactions. Hence, conversational AI overcomes the challenge of providing limited responses by enhancing its understanding of user inquiries.
Transformative Trends in the Generative AI Market
The generative artificial intelligence market has seen remarkable growth and transformation in recent years. One major trend in the market has been an increased focus on improving user experiences through generative AI-based tools and applications. These applications have been efficient in gaming, entertainment, and design.
The increasing demand for generative artificial intelligence applications is witnessed in various sectors, primarily driven by technological advancements like super-resolution, text-to-image generation, and text-to-video conversion. Additionally, there is a pressing need to streamline workflow processes within organizations, contributing to the surge in demand for such applications. The need for AI-driven solutions to extract meaningful insights from this data has become more pressing. Prediction algorithms have proven highly effective in analyzing complex datasets, identifying patterns, and generating valuable predictions.
Advanced generative models, including Deep Convolutional GANs (DCGANs) and StyleGANs, have significantly impacted the market, generating high-quality and realistic images and videos. This has had implications for industries such as entertainment, gaming, and visual content creation. Generative AI is also increasingly used for automated content creation and curation, benefiting domains such as social media, marketing, and journalism, where AI-generated content can streamline processes and improve content relevance and engagement.
Finally, artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics significantly shape the generative AI market. For example, Using artificial intelligence (AI) can streamline the process of detecting potential malignancies at an early stage, thereby enabling healthcare professionals to devise more efficient treatment strategies. In addition, the growing demand for AI-powered chatbots to enable effective conversations and boost customer satisfaction is another significant growth-inducing factor for the market.
Key Drivers of Generative AI Value Chain
A new value chain is emerging to support the training and utilization of generative AI systems as they continue to develop and be deployed.
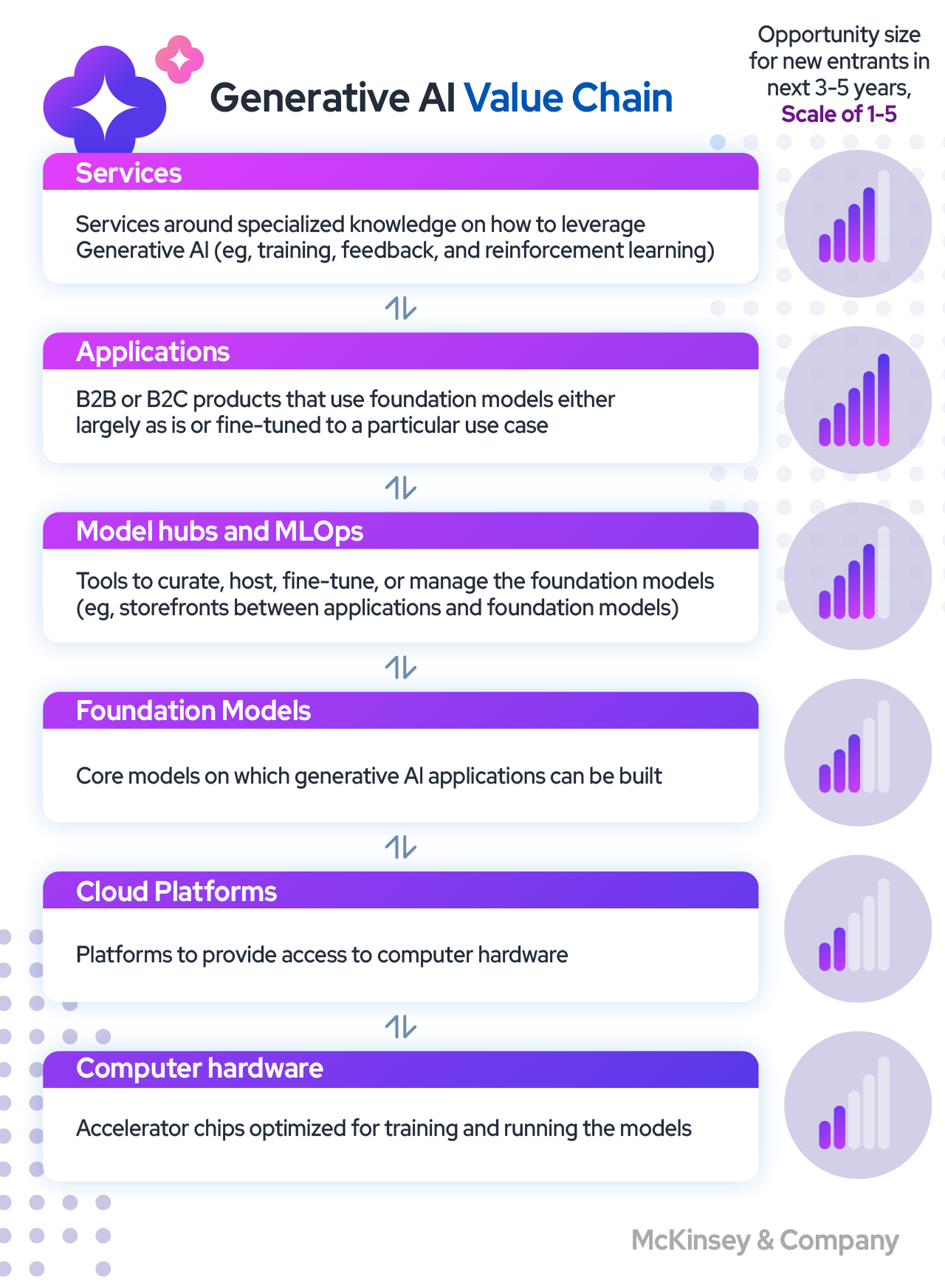
1. Computer hardware
Massive quantities of data are essential for generative AI systems to generate content, a task that conventional computer hardware cannot handle. Extensive clusters of GPUs or TPUs equipped with specialized accelerator chips are required to process the vast amount of data across billions of parameters simultaneously. The chip design market is largely dominated by NVIDIA and Google, while TSMC is responsible for producing nearly all accelerator chips. However, new entrants into the market encounter significant initial expenses for research and development. At the same time, traditional hardware designers must acquire specialized expertise, knowledge, and computational capabilities to cater to the generative AI industry.
2. Cloud platforms
GPUs and TPUs are costly and scarce, making it impractical for most businesses to possess and maintain this vital hardware infrastructure on-premises. As a result, most of the work to create, fine-tune, and operate large AI models occurs in the cloud. This allows companies to access computational power and manage their expenses as needed quickly. The leading cloud providers possess the most extensive platforms for executing generative AI workloads and enjoy exclusive privileges about hardware and chips. Specialized cloud challengers will likely gain market share shortly with the support of a large enterprise looking to reduce its reliance on hyperscales.
3. Foundation models
Foundation models are the backbone of generative AI. They are large deep-learning models pre-trained for creating specific types of content and can be modified for various tasks. These models have undergone training using vast datasets, including publicly unlabeled data obtained from different sources and privately obtained data from significant databases. Developing foundation models requires expertise in several areas, such as data preparation, model architecture selection, training, and tuning. However, the training cost for foundation models is currently high, which limits the market to a few tech giants and start-ups backed by significant investment. Nevertheless, there is ongoing work to make smaller models to deliver effective results for some tasks and more efficient training, which could open the market to more entrants.
4. Model Hubs and MLOps
Businesses seeking to develop applications using foundation models need a platform to store and retrieve the model and specialized MLOps tools and technologies to customize and implement the model in their end-user applications. Model hubs serve as a gateway for closed-source models, offering various services for open-source models. These hubs may encompass model aggregators or comprehensive MLOps capabilities, enabling businesses to optimize and deploy foundation models seamlessly into their applications. Developing and deploying multimodal foundation models require sophisticated tools and platforms capable of handling complex datasets and training processes.
5. Applications
In many different industries, generative AI may increase productivity and economic efficiency. The most promising domains for generative AI applications are information technology, marketing and sales, customer support, and product development. IT teams can gain from automated documentation and code. Customer service can utilise virtual assistants and personalised chatbots to answer natural language requests and customer inquiries. At the same time, marketing and sales teams can use generative AI to develop customer outreach content. Generative artificial intelligence (AI) can lead to major operational efficiencies in various industries, including media and entertainment, banking, consumer goods, telecommunications, life sciences, and technology.
6. Services
Companies will use dedicated generative AI services to fill capability gaps and navigate business opportunities and technical complexities. Existing AI service providers will expand their capabilities to serve the generative AI market. Specialized niche players will enter the market with knowledge of applying generative AI to specific functions, industries, or capabilities.
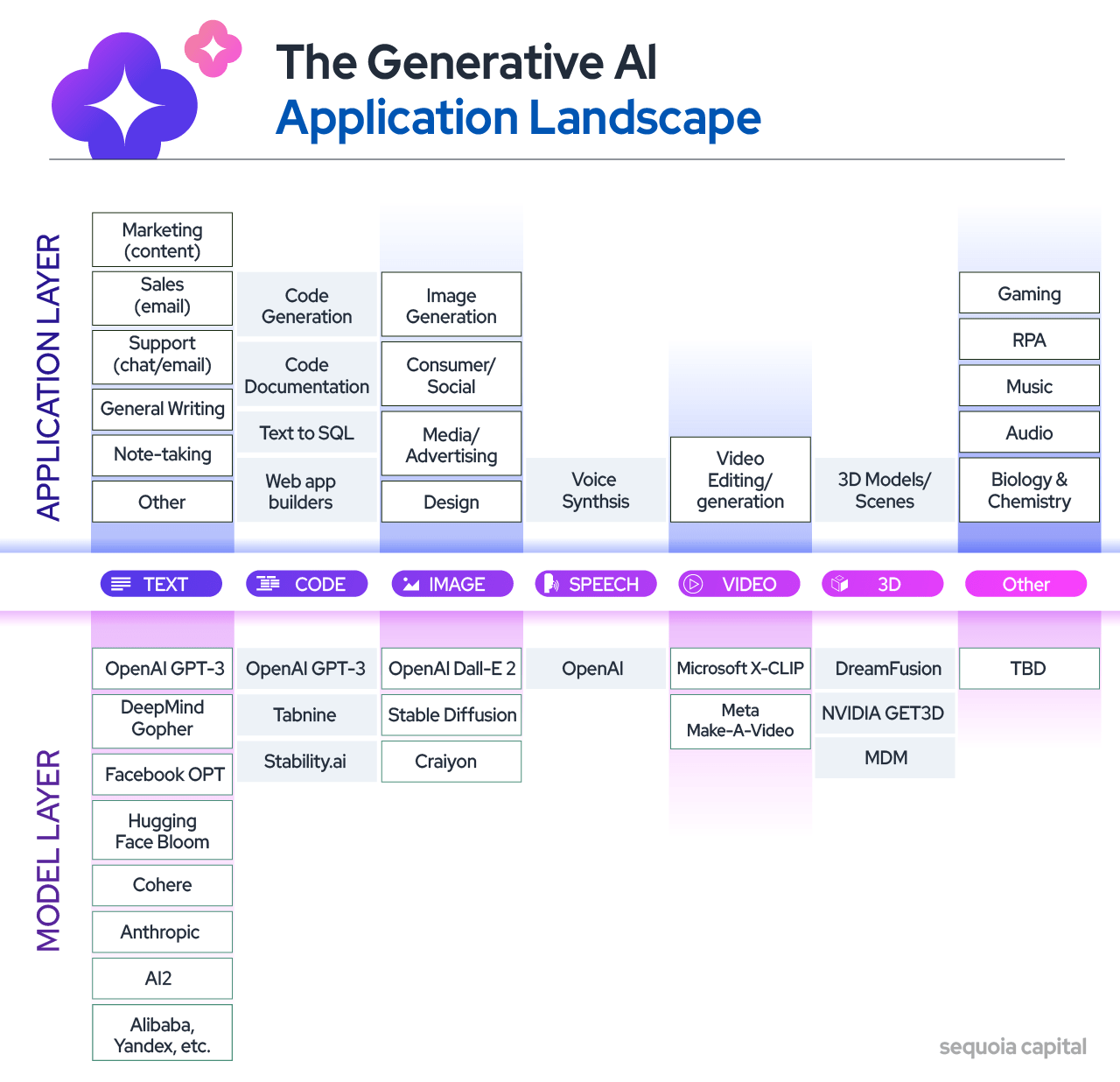
Generative AI Landscape Categories
Generative AI can be divided into text-based applications, image, music, and video generation. Researchers are exploring new ways to improve generated content quality and apply the technology across domains like art, gaming, and advertising. With exciting possibilities for the future, generative AI has the potential to revolutionize multiple industries
1. Text: summarizing or automating content
AI-generated content may quickly produce multimedia content using already-existing data. Marketers use it for newsletters, emails, and branding. AI text generators use large datasets to extract and select the best output. Use content writing, chatbots/assistants, analysis/synthesis, and website conversion rates to boost sales, marketing, talent acquisition, and website conversion.
- Use content writing for personalized emails/posts, interview questions/job descriptions.
- Employ chatbots to boost website conversion rates
- Improve natural web search through analysis and synthesis
- Utilize content writing to improve sales
- Summarize legal documents for risk and legal purposes.
2. Code: Generating code
Many generative AI applications are available for multilingual code generation through text inputs. They can be used as coding assistants and generate code based on context and syntax. Some famous examples include Alphacode, Amazon Codewhisperer, CodeGeeX, and GitHub Copilot. These applications can also be personalized to match the writing style. Generative AI technologies are also used for coding documentation, Excel spreadsheet code generation, SQL code generation, code translation, website and app creation, and even natural language cybersecurity analysis. There are also emerging technologies such as design-to-code and text-to-automation tools.
- Code generation accelerates app development with automatic code recommendations.
- Quickly generate user interface designs with our application prototype and design tool.
- Generate synthetic data sets to improve AI model quality.
3. Images: Generating images
Brands are using generative AI to create images for commercial use, saving time and money. It allows for initial concept creation and design that human professionals can perfect. AI is also helpful for image editing, filling in gaps where customers do not have a physical package but have the art, and generating photo-realistic representations of products.
- A stock image generator can generate unique media for marketing and sales.
- An image editor can help personalize content quickly for marketing and sales purposes.
4. Audio: Summarizing, generating, or converting text into audio
Integrating large language models and text-to-image generation improved AI-powered audio generation quality. Speech synthesis models have advanced to the point where they can generate voices that are virtually indistinguishable from human voices. Similarly, music generators have made significant progress in creating realistic melodies and harmonies, all based on textual or melodic prompts.
- For educational purposes, voiceovers are generated for training.
- Unique sounds are designed for entertainment while avoiding copyright infringement.
- Podcast recordings are modified and refined in post-production without re-recording.
5. Video: Generating or editing videos
Generative Video Models have advanced significantly and have many practical applications, such as editing, creation, and video production. They can optimize the design process and help create photorealistic videos with digital humans.
Video creation
- Using AI avatars to create engaging and interactive video lessons, revolutionising training and corporate presentations.
Video editing
- Maximizing engagement on social media by editing videos to be shorter and more attention-grabbing.
- Adding personalization to generic videos enhances customer experience and engagement with the brand.
Video translation
- Dubbing videos
- Providing live translations
- Creating voice clones
Face swaps and adjustments
- Visual Effects
- Lip Synchronization
- Real-time gaze correction during video conferencing
6. Chatbots: Automating customer service and more
Large language models, such as ChatGPT, have transformed AI with their capabilities in natural language processing. They can perform tasks such as summarization, writing assistance, code generation, language translation, and sentiment analysis. Customer service applications powered by LLMs have gained significant attention and can be used for demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and risk management in business operations.
7. ML platforms: Applications / ML platforms
LLMOps is a refined version of MLOps that focuses on managing large transformer models and monitoring them at scale. LLMOps has been added to Microsoft’s Azure Machine Learning platform, providing enhanced capabilities for managing large transformer models. Additionally, developers can access a central hub in our model catalogue to discover, customize, and deploy pre-trained AI model solutions, including our new open-source vision models for image classification, object detection, and image segmentation. These powerful vision models can be integrated into applications for predictive maintenance, intelligent retail solutions, and autonomous vehicles.
8. Search: AI-powered insights
Organizations use AI-powered knowledge management systems to gather and distribute relevant information for insights.
- AI can aid HR departments by generating job descriptions, identifying required skills, and classifying applicants.
- AI technology such as RAG, summarization, and classification can improve customer service by providing personalized support, searching for answers in internal documents, and identifying customer problems and sentiments.
- Summarizing business objectives and knowledge can help developers focus on coding, while generative AI can assist developers in generating code and increasing ideation.
9. Gaming: Gen-AI gaming studios or applications
Generative AI technologies have the potential to greatly enhance the gaming industry by helping to create 3D models, storytelling, and characters.
- Various applications such as CSM, Illiad AI, and Latitude are already utilizing Generative AI for videogame creation.
- Pixelvibe and Armorlab also aid in creating game assets and textures through AI-powered software.
- MarioGPT models are now available for Open-Ended Text-to-Level Generation with LLMs.
10. Data: Designing, collecting, or summarizing data
Generative AI can help bridge the knowledge gap by converting data patterns into plain language, providing enriched context through historical comparisons, and boosting time efficiency by automating the generation of basic insights and summaries. Its ability to narrate stories can enhance decision-making, offering businesses a clearer view of potential site benefits and challenges.
11. Customer Emails Tools
AI-generated content may quickly produce multimedia content. Marketers use it for newsletters, customer email tools, and branding. AI text generators use large datasets to extract and select the best output.
12. Accessible Content Generation Tools
The emergence of accessible content generation tools is bound to revolutionize how content is created. It is expected to transform text and images, hardware designs, music, videos, and more. Consequently, people must focus on content editing instead of content creation, which demands different skills. Moreover, the way users interact with applications will change with the advancement of AI models. They will become more conversational, proactive, and interactive.
Impact of Generative AI on Different Functions Across Industries
Implementing Generative AI Applications and Use Cases is expected to impact different industry functions. The impact will vary depending on several variables, including the degree of automation and the kind of work that other functions are performing.
1. Sales and Marketing
The rise of gen AI can impact marketing and sales in three areas: Customer experience, growth, and productivity. Gen AI can create hyper-personalized content for Customer experience, jumpstart growth by providing sales teams with analytics and customer insights and automate mundane sales activities to free up time for customer interactions. Gen AI can also optimize marketing strategies and automate lead-nurturing campaigns. Personalised messaging and content, in-the-moment negotiation advice, and onboarding for new clients are all possible with Gen AI.
2. Customer operations
Generative AI can transform customer service by improving productivity and providing personalized support. Here are five ways it can make a difference:
- Conversational Search – Customers can quickly get relevant information in their preferred language.
- Agent Assistance – Automate responses and summaries, empowering agents to provide better support.
- Build Assistance – AI can generate content and suggestions for customer service tools.
- Call Centre optimization – AI analyzes the data and provides insights to improve performance.
- Personalized Recommendations – AI considers customer history to provide tailored information in their preferred format.
3. Product and R&D
Generative AI has a broad range of applications in product research and development. It can be utilized to design optimized parts to meet specific goals and constraints. Moreover, it is also helpful in creating new products faster, including new drugs, less toxic household cleaners, novel flavors and fragrances, new alloys, and better diagnoses. Generative design systems can explore many potential solutions, comparing the outcomes of thousands of simulations to arrive at a design that delivers the most favourable results.
4. Software Engineering
Generative AI can enhance software development by facilitating low-code solutions, streamlining cybersecurity with integrated AI, accelerating digital transformations and remote work, generating code sections, identifying errors, suggesting code modifications, and optimizing performance.
5. Supply Chain and Operations
Generative AI is useful in supply chain management for demand forecasting, supply chain optimization, and automating clerical work. It can analyze historical sales data, optimize various supply chain stages, predict operational results, and factor tariffs into operational costs.
6. Risk and Legal
Generative AI has several potential legal use cases, including compliance and regulatory monitoring, contract analysis and negotiation, document drafting and review, due diligence, intellectual property management, legal research, and legal chatbots. These applications can help businesses remain compliant with regulations, improve contract negotiations, automate document drafting, identify potential risks, protect intellectual property, conduct legal research more efficiently, and provide essential legal guidance to clients.
7. Strategy and Finance
Generative AI has numerous applications in finance. It can produce educational and financial scenarios, manage portfolios, simulate risks, identify fraud, analyse financial data, produce customised financial reports, and give enterprise operations contextual knowledge. Finance professionals may also be able to refocus on higher-value tasks like strategic planning and analysis.
8. Corporate IT
Generative AI is widely used in businesses to enhance human creativity and speed up innovation. It can drive operational efficiency, create compelling marketing campaigns, detect fraud, generate realistic virtual agents, automate customer support and sales development, and create marketing content.
9. Talent and Organization
Generative AI is a powerful tool for transforming talent management. It allows for accurate evaluation and prediction of team member performance, personalized training programs, data-driven job requirements, and assistance for employees and hiring managers. Its impact can be felt across job design, HR practices, and talent management.
10. Designing (Fashion)
Algorithms are used in generative AI to produce distinctive and varied visuals that combine human creativity with computer-generated styling. This approach to creating visual art allows for infinite variations of the same image with no limitations on cost or resources. Generative AI perfectly matches the fashion industry, which relies on creativity, style, and uniqueness. AI-generated images are almost indistinguishable from real ones and are perceived as more novel than original ones. Generative AI has numerous applications in the fashion sector, such as creating virtual fashion models, converting sketching into colour graphics, and creative designing.
11. Complete stack Applications (Legal, Biotech, Finance)
Generative AI technologies are proving to be of immense help in biotech, particularly in molecule modelling, drug discovery, and protein modelling. The advancement of these technologies is happening at a fast pace, and they hold the potential to enhance the accessibility of biotech solutions greatly.
12. Consumer Avatar and Face Apps
Generative AI is widely used in the entertainment, advertising, and graphic design industries to speed up creative processes and create personalized experiences for audiences. It enables streaming services to generate personalized movie titles and visuals and create unique artwork for TV series based on a user’s viewing history and preferences. Using generative AI models like Stable Diffusion, personalized avatar solutions can generate avatars based on any text prompt after fine-tuning the model with 10–12 user images.
13. Multilingual dubbing
Generative AI is transforming the creation and translation of multilingual multimedia content. AI-driven technologies have now automated the workflows for captioning and subtitling, reducing time and guaranteeing accuracy and consistency across languages. AI models can mimic human voices, offering diverse, multilingual audio that matches studio-quality recordings. LLMs are advancing in their linguistic capabilities, improving the quality of translated content. However, human oversight is crucial to maintaining rigorous quality control, ensuring accuracy, cultural sensitivity, and context relevance.
Major Industries Impacted Across the Landscape
- High tech
- Entertainment and Media
- Healthcare
- Automotive
- Retail and E-commerce
- Banking and Finance
- Manufacturing
Approach to Building Generative AI Applications
The emergence of generative AI is bound to revolutionize how content is created. It is expected to transform text and images, hardware designs, music, videos, and more. Consequently, people must focus on content editing instead of content creation, which demands different skills. Moreover, the way users interact with applications will change with the advancement of AI models. They will become more conversational, proactive, and interactive. This will necessitate a redesigned user experience that revolves around suggestions and recommendations. Although this may boost productivity, it will also challenge the conventional notion of human-led strategy development.



