Introduction to Agentic Process Automation (APA)
Agentic process automation (APA) is changing how businesses operate as a functional integrator of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) to produce autonomous, intelligent workflows. Uniquely to APA, we introduce AI agents that can make decisions, learn from data, and adapt to changes in the environment. Despite its potential transformational power, this innovation requires a profound grasp of the challenges it poses and the use of best practices.
This blog shares the challenges of APA, highlights the need for best practices, and offers actionable tips for businesses that want to capitalize on APA’s potential.
Transforming Business with Agentic Process Automation
From static automation to dynamic, intelligent business operations, this is a new paradigm in business operations. By integrating AI agents into workflows, organizations can achieve:
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automated processes reduce manual intervention through the capability and automation of complex multi-step processes.
- Improved Decision-Making: The real-time data analysis capabilities of AI agents allow for actionable insights and smarter decisions through the use of decision-making algorithms.
- Scalability: With its adaptability, businesses can scale up or down operations without the need for concomitant increases in resources.
- Cost Savings: APA wastes less effort, reduces operational costs, and minimizes errors, thereby increasing operational efficiency.
The APA results are transforming output in industries like healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing, from predictive maintenance and fraud detection to personalized customer experiences and better supply chain management.
Key Challenges in Implementing APA Successfully
While Agentic Process Automation (APA)’s potential is undeniable, its implementation comes with significant challenges that businesses must address proactively: ensuring the decisions made by AI agents are reliable and aligned with organizational goals.
Ensuring Reliable Decision-Making
The autonomy of AI agents is central to APA. These agents must make accurate decisions that align with the organization’s objectives and long-term strategy.
Key challenges include:
- Understanding, and in some cases eliminating, biases in AI models to prevent them from affecting decision-making algorithms.
- Running AI agents in a diversity of real-world scenarios to ensure their adaptability in multi-agent systems.
- Measures to validate decisions, potentially with human oversight, to ensure autonomous decision-making remains aligned with operational standards.
Data Privacy and Security
Given that APA often processes sensitive and confidential data, data privacy and data security are essential. Organizations must prioritize these aspects to prevent breaches and unauthorized access.
Key challenges include:
- Preventing such data from being breached and accessed without permission requires stringent security measures and compliance with regulations such as GDPR or CCPA.
- Implementing encryption, access controls, and regular security audits to keep your data privacy and security in check, ensuring alignment with ethical AI practices.
Navigating Complexity
The complexity of APA increases within workflows as models based on AI and machine learning are integrated. Automation technologies such as Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) and Generative AI (GenAI) add another layer of sophistication.
Key challenges include:
- Showcasing single-point defined solutions that align with existing systems and infrastructure, ensuring seamless integration with current technologies.
- Teaching teams to work effectively with APA technologies, especially in managing agentic workflows.
- Ensuring APA’s scalability and flexibility to accommodate growth, both in resources and operational needs.
Ethical Considerations
The implementation of APA raises important ethical concerns, particularly around AI decision-making. Ensuring transparency and accountability in AI actions is critical for the responsible use of automation technologies. Addressing these issues helps build trust and promotes ethical APA practices.
Key challenges include:
- Reducing and improving biases reflected in AI algorithms for fairness and inclusivity in decision-making.
- Building transparency into decision-making processes to ensure that actions taken by AI agents can be understood and traced.
- Ensuring that AI-driven actions are accountable and that autonomous decision-making follows ethical guidelines, minimizing risk to businesses and society.
Why Best Practices are Crucial for APA
Given the challenges of Agentic Process Automation (APA), best practices are crucial to ensure its effectiveness, sustainability, and successful integration into business operations. These practices provide:
- Guidance: A clear roadmap for navigating the complexities of APA and avoiding common pitfalls.
- Efficiency: Streamlined workflows that reduce errors and redundancies, driving better operational outcomes.
- Trust: Confidence among stakeholders by ensuring ethical, transparent, and accountable use of APA.
- Scalability: Robust frameworks that allow for growth and flexibility, adapting to the evolving needs of the business.
Top Best Practices for Effective APA Implementation
To unlock the full potential of Agentic Process Automation (APA), businesses should adopt the following best practices:
Define Clear, Specific Goals: Establishing clear, specific goals ensures that APA initiatives are aligned with organizational objectives. For example, if the goal is to enhance customer satisfaction, workflows should prioritize tasks that improve customer interactions, such as faster response times or personalized recommendations.
Leverage Specialized AI Agents: Utilize AI agents with distinct skill sets to handle specific tasks. Collaboration between these specialized agents can drive efficiency. For example, in healthcare, a data analytics agent can assess patient records while a scheduling agent manages appointments, creating a seamless patient care process.
Keep Humans in the Loop: Balancing autonomy with oversight is crucial for successful APA implementation. Human involvement ensures that AI decisions align with business goals and ethical standards. Regular reviews and validations help prevent errors and reinforce trust in APA systems.
Foster Multi-Agent Collaboration: Enable AI agents to communicate and collaborate effectively within multi-agent systems. In a supply chain scenario, a stock monitoring agent could coordinate with a supplier management agent to ensure timely replenishment of inventory, boosting agility and responsiveness.
Implement Rigorous Data Governance: Establishing robust data governance practices is essential for maintaining transparency and accountability in APA. This includes:
- Tracking data interactions with metadata.
- Creating audit trails to monitor data usage and transformations.
- Enforcing clear data privacy policies and compliance standards, ensuring alignment with ethical AI practices.
Partner with Experienced Vendors: Collaborating with vendors who understand AI technology and the nuances of your industry can streamline APA implementation. Their expertise can help address technical challenges, optimize workflows, and ensure the system is scalable and adaptable to future needs.
Unlocking the Benefits of APA
When implemented effectively, APA offers numerous benefits that can transform business operations:
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlined processes reduce manual effort and errors, enhancing overall productivity.
- Real-Time Insights: AI agents analyze data instantly, providing actionable insights that enable better and faster decision-making.
- Cost Reduction: Automation minimizes resource wastage and cuts down operational costs, leading to greater profitability.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Personalized, timely interactions boost customer satisfaction and foster long-term loyalty.
- Scalability: APA’s adaptability supports growth without requiring a proportional increase in resources, making it scalable.
- Resilience: Multi-agent collaboration ensures business continuity and adaptability in dynamic, changing environments.
Key Elements of an Effective APA Implementation Strategy
Defining Clear Objectives and Goals
Before implementing Agentic Process Automation (APA), it’s essential to define what you hope to achieve. The goals could range from reducing operational costs to enhancing customer experience. Understanding the key performance indicators (KPIs) and desired outcomes will guide the entire implementation process.
Example: If your goal is to improve customer service, you could use APA to automate customer queries, allowing agents to address customer issues in real time and ensuring dynamic business operations with the help of intelligent document processing (IDP).
Choosing the Right Automation Tools and Platforms
Selecting the right tools and platforms is critical to ensuring a smooth implementation. Tools like Apache Kafka for event-streaming, TensorFlow for machine learning, and cloud-based platforms like AWS or Azure can enhance the flexibility of APA solutions. Consider incorporating Generative AI (GenAI) and Large Language Models (LLMs) to power autonomous decision-making.
Example: In a manufacturing setting, tools like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can be integrated with APA to automate the movement of materials between different departments, enhancing operational efficiency through multi-agent systems.
Building a Robust Data Infrastructure
Data is the backbone of Agentic Process Automation. A strong, organized data infrastructure ensures that agents have access to accurate, timely information. This may involve integrating various data sources, such as CRM systems, databases, or IoT devices, to enable seamless decision-making and real-time data analysis.
Example: A customer service agent can access real-time inventory data to provide customers with up-to-date product availability information while maintaining data privacy and security through ethical AI practices.
Designing Agent-Centric Workflows
A successful Agentic Process Automation implementation is built on agent-centric workflows that are both efficient and adaptable. This involves designing workflows that assign tasks to autonomous agents based on predefined criteria and continuously optimizing these workflows for better performance, ensuring predictive maintenance and streamlined task execution.
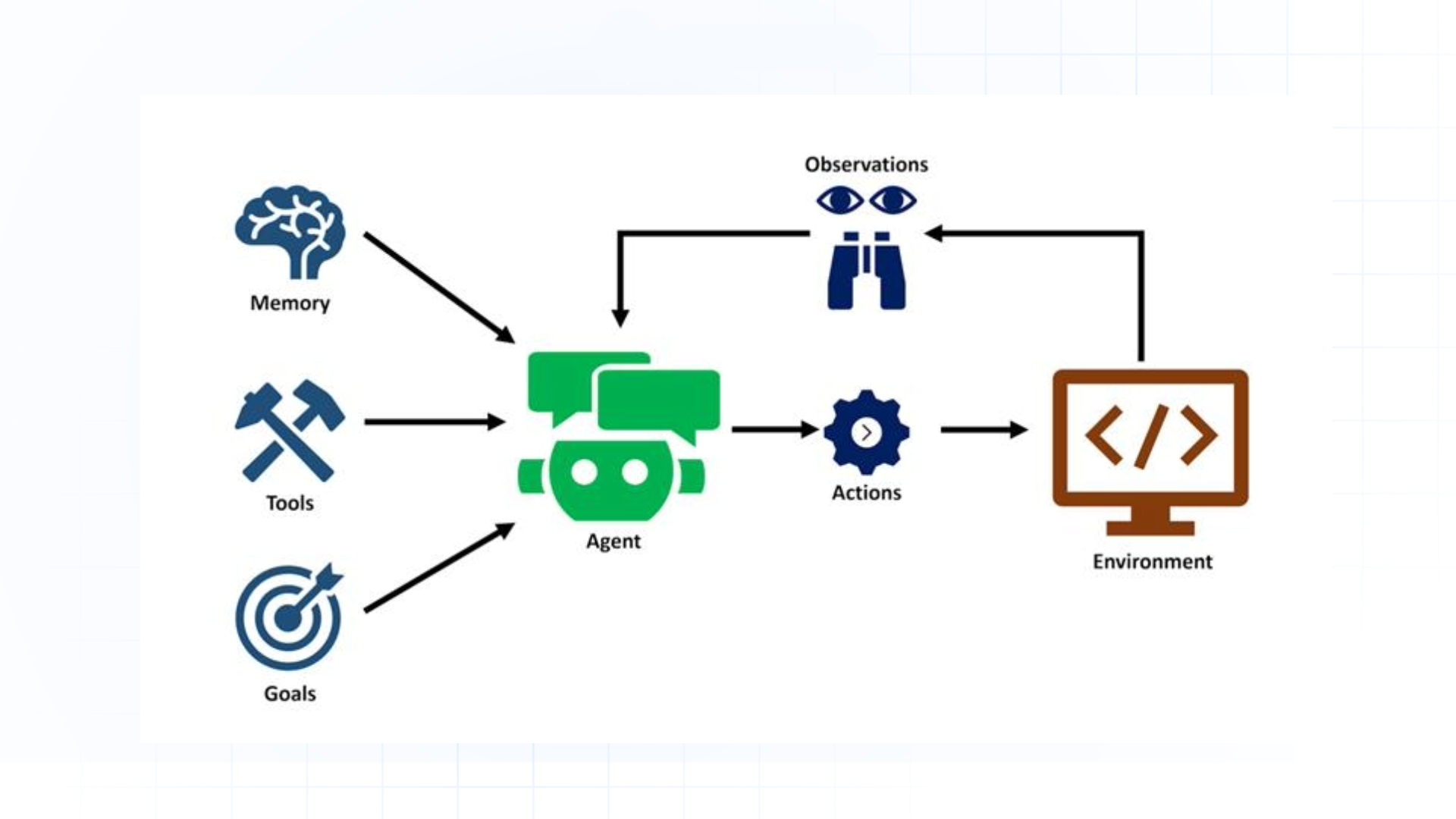
Example: In a supply chain, a logistics agent can monitor delivery status, communicate with vendors, and update systems automatically when delays or changes occur, enhancing dynamic business operations.
Leveraging Machine Learning for Continuous Improvement
Machine learning algorithms enable agents to learn from data and improve their decision-making capabilities continuously. Implementing machine learning models allows agents to optimize workflows and adapt to new situations without requiring manual reprogramming, leading to improved automation technology and increased operational efficiency.
Example: In a sales process, agents can analyze customer behavior patterns to predict the best time to send promotional emails, thus improving engagement rates by incorporating Natural Language Processing (NLP) for better customer interaction.
Ensuring Scalability and Flexibility
An effective APA strategy must be scalable to accommodate future growth. As business needs change, so should the capabilities of the automation system. Cloud infrastructure, microservices architecture, and modular design help ensure that Agentic Automation solutions can grow with your business, enabling the implementation of more agentic workflows over time.
Example: A company starting with basic customer query automation might later scale to fully autonomous agents managing end-to-end product delivery with the help of multi-agent systems for optimized task distribution.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Once the system is live, constant monitoring is necessary to ensure that the agents perform as expected. Key metrics such as task completion time, error rates, and overall system efficiency should be tracked. Continuous evaluation will also help fine-tune the models for enhanced performance, ensuring autonomous decision-making.
Example: In a customer service setup, agents can be monitored for response times and resolution accuracy. Tracking these metrics allows for adjustments to improve task execution and overall performance.
Security and Compliance Considerations
Implementing APA requires attention to data privacy security and regulatory compliance. Ensuring that agents handle sensitive data in accordance with privacy laws (e.g., GDPR) is essential for building trust and maintaining legal integrity, particularly in industries such as healthcare and finance, where ethical AI practices are critical.
Example: In a healthcare setting, an agent managing patient records must ensure compliance with HIPAA regulations, protecting patient data privacy while ensuring data privacy and security are maintained throughout the agentic process automation implementation.
Effective Strategies for Implementing APA Solutions
To successfully implement APA across industries, businesses should follow strategic approaches that foster smooth adoption and long-term success.
Create an Automated Center of Excellence (CoE): A Center of Excellence (CoE) provides a foundation for governance, best practices, and technical expertise, ensuring the effective implementation of APA. Steps to establish a robust CoE include:
- Forming an executive committee dedicated to automation.
- Drafting a Charter of Excellence to define goals, values, and roles.
- Establishing a centralized governing body to oversee and maintain governance.
- Building a CoE team with experts from AI, data science, IT, and DevOps.
- Continuously monitoring and refining the CoE’s activities to improve outcomes.
Promote Early Automation Success: Building a culture that embraces automation is crucial. To foster enthusiasm for APA, the following strategies can help:
- Creating a portal to track internal automation requests and ROI.
- Celebrating key milestones and successes in automation initiatives.
- Organizing automation events to brainstorm and develop new ideas.
- Offering eLearning programs to educate employees on the role and benefits of APA.
Adopt an Agile Approach to Development: Utilizing agile methodologies accelerates the development of APA solutions. By breaking workflows into smaller components, businesses can implement intelligent workflows more quickly, enabling iterative improvements and faster deployment.
Integrate AI-Centric Capabilities: To unlock more advanced benefits beyond basic automation, integrating AI agents within workflows enables real-time interactions and decision-making. Key components include:
- Intelligent Workflow Management: AI agents adapt processes based on real-time data and predicted outcomes.
- Advanced Decision-Making: Autonomous agents provide contextual insights, improving operational control and guiding the next steps.
- Collaborative AI Agents: Agents work together to optimize end-to-end processes, ensuring efficiency.
- Adaptive Learning: Autonomous agents learn from ongoing data, continuously improving their decision-making capabilities.
- Anomaly Detection: AI agents identify irregular patterns and automatically trigger corrective actions.
Keep Humans in Charge: Automation should enhance human potential, not replace it. Human oversight is critical to aligning APA with business goals. Equip employees with real-time data for informed decision-making and foster a collaborative environment where humans and AI agents work together seamlessly.
Navigating the Future of APA
Agentic Process Automation (APA) is a game changer, enabling organizations to achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, innovation, and scalability. However, its successful implementation requires careful planning, consideration of ethical implications, and adherence to best practices. Businesses that proactively address these challenges, align APA with established guidelines, and remain committed to continuous improvement can unlock their full potential, build trust, maintain compliance, and foster sustainable growth.
As industries evolve, APA will remain at the forefront of innovation, empowering organizations to meet their goals with intelligence, agility, and confidence.



