Computer Vision, a branch of Artificial Intelligence, allows machines to see, interpret, and make sense of their surroundings using machine learning techniques.
Brief Overview of Computer Vision
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a general research field that includes Computer Vision (CV), a specialized area that aims to make machines understand visual data from images and videos. ‘To see’ with computers, robots and automated systems, CV technology seeks to equip them with the ability to capture camera or sensor input, process it, and analyze it as humans perceive it. The idea is to teach these systems to recognize visual cues and make data-driven decisions, interpreting their environment to perform tasks requiring visual understanding.
Key Components and Processes in Computer Vision
This blog will examine the fundamental pieces and processes that power computer vision technology.
Key Components in Computer Vision
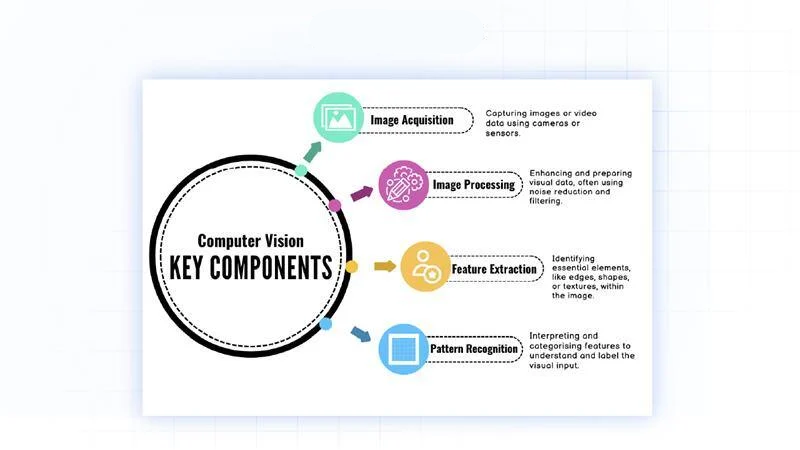
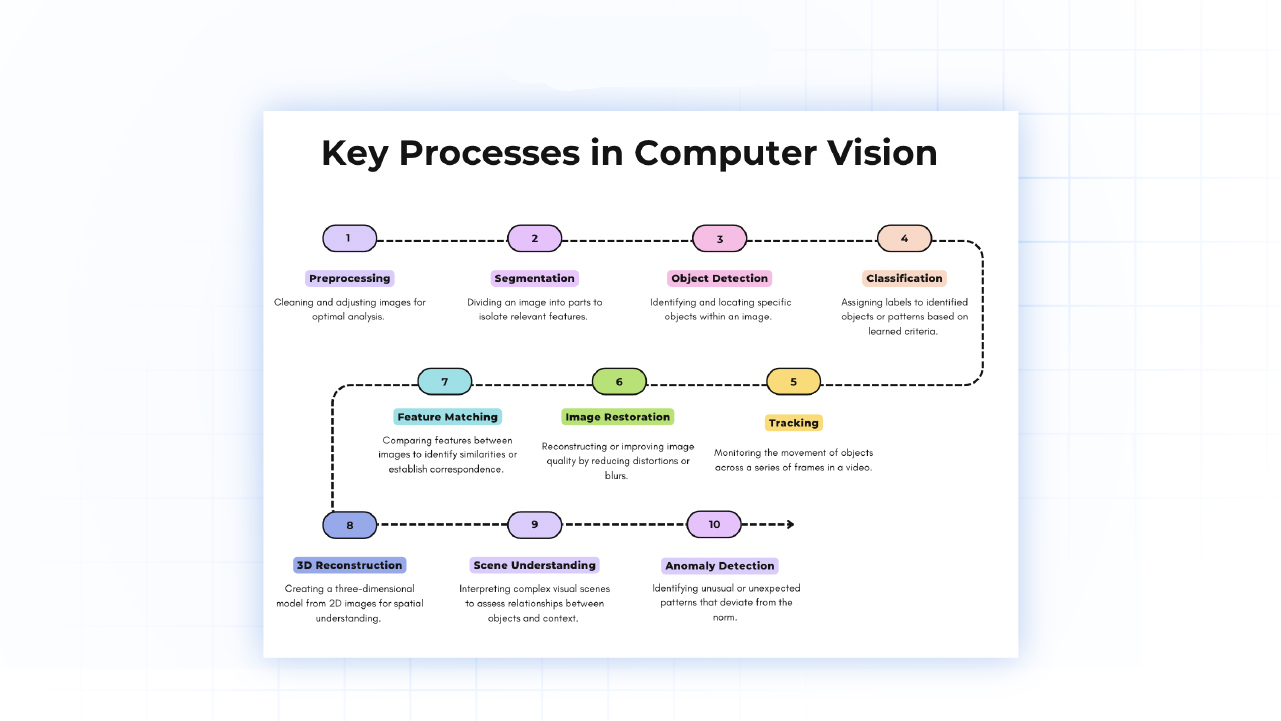
Key Processes in Computer Vision
Next, let us look at the main processes used when implementing computer vision.
Capabilities of Computer Vision
Computer vision unlocks many capabilities for machines, allowing automation across many operations.
- Object Classification: This process involves categorizing objects in an image according to labels or groups. For example, with object classification, a computer can tell which people are in an image and how many people are in the image.
- Object Identification: This step is more than classification; it identifies specific objects in an image or video. For example, the system can not only identify objects in a photo but can examine the characteristics of the people in the photo to infer identity or traits.
- Object Tracking: In this case, the system monitors the position of a moving object over time in a video sequence. For instance, in a parking lot, surveillance cameras can record the location and movement of a vehicle over time.
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR): The process of detecting letters and numbers in images and converting them into machine-readable text that other applications can use or modify.
Working on Computer Vision
Let’s look at how computer vision works at its core steps
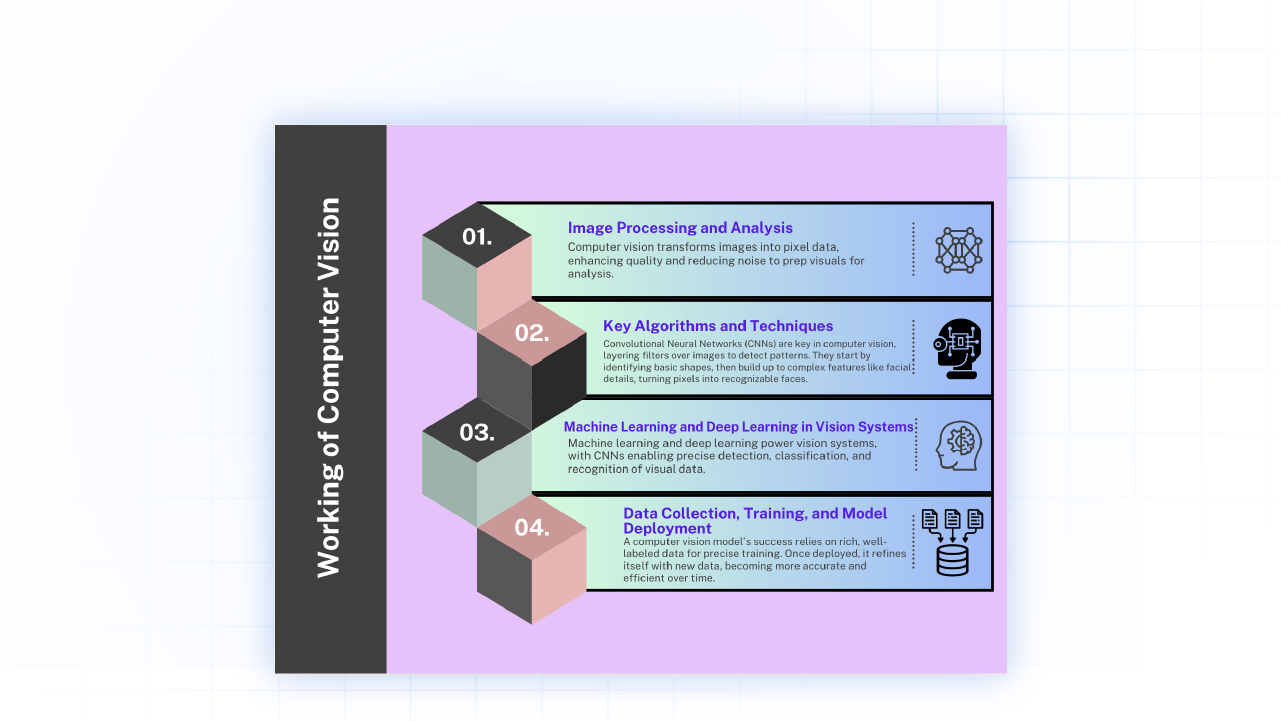
Usages of Computer Vision
Computer vision is part of everyday life: from basic tasks to highly complex systems. In this section, let’s explore its use cases across different industries and practical scenarios.
- Content Organization: Computer vision-based content organization is the process of analyzing and categorising visual media. It can help you sort, scan, and tag images and videos for massive amounts of media in an orderly and easy-to-find way. Platforms that manage lots of visual content, such as social media and e-commerce sites, find this particularly useful.
- Text Extraction: Computer vision is a technology that extracts text from images and scanned documents and uses optical character recognition (OCR) to convert it into editable digital text. It allows you to digitize paper documents, automate data entry, and make the text searchable – very useful for industries where document management and data processing are crucial.
- Augmented Reality: Computer vision in augmented reality (AR) allows digital objects to be anchored into the real world by associating them with surfaces and objects. This makes AR experiences more immersive because users can interact with virtual elements in a real-time environment, which is useful for applications in gaming, retail, and training simulation.
- Agriculture: Drone and satellite imagery help computer vision improve agricultural areas by monitoring crop health, detecting weeds, and analyzing soil quality. Using visual data analysis, farmers can not only maximize their crop yields but minimize resource waste, as well as identify problems so they can help drive more sustainable farming practices.
- Healthcare: In healthcare, computer vision is used to help analyze medical imaging (patterns of X-rays, MRIs, etc.) to detect anomalies – such as tumours or fractures. It helps to accelerate diagnosis and precise treatment, even with real-time visual data available to surgeons during procedures, constituting a valuable medical diagnostic and treatment tool.
- Sports: Computer vision is used in sports for performance analysis and planning. Players can use it to monitor their movements, work out tactics in the game, and even draw player positioning and choices. Industry insights like these can help athletes and coaches be better performers, improve tactics, and give fans better gaming experiences.
- Manufacturing: Computer vision is used in manufacturing to help with quality control by looking at the products, going down the lines to inspect them, and seeing if they are defect-free and meet some given specifications. Additionally, it supports automation, which is necessary for machines with vision abilities, which can monitor workflows, check equipment status, and play a role in increasing overall efficiency.
- Spatial Analysis: Taking advantage of computer vision, the placement of objects can be understood spatially and studied to facilitate mapping and navigation tasks. Its use includes urban planning, autonomous vehicle navigation, and logistics where the spatial relationship between objects must be understood.
- Face Recognition: Face recognition is a process by which computer vision confirms identities using facial features. This technology has become widely used in security and authentication systems and enables contactless verification in many situations, including smartphone access verification, secure facility entry, and personalized customer experience.
Future of Computer Vision Technology
1. Real-Time Edge Processing: Computer vision with edge AI and 5G is faster and more reactive, making possible instant applications in things such as autonomous vehicles, live monitoring and event analysis.
2. Seamless IoT Integration with Vision Agents: Today, vision agents help blend IoT environments to perform tasks such as image capture, analysis and recognition within smart cities, homes and industries, to make them work better and work together.
3. Advanced AI and Specialized Deep Learning: Higher precision AI models enable vision agents to extract sophisticated data like emotions or contextual cues, enabling them to provide high precision in demanding applications.
4. New Frontiers in AR and Robotics: Vision Agents enable potential in AR, robotics and autonomous systems to provide real time video processing, interactive AR and autonomous navigation, bringing new levels of immersion and autonomy.
5. Ethical and Privacy-Centric Solutions: Robust security and ethical standards, responsible data use, and privacy safeguards make future-ready vision all that and give always progress to computer vision.
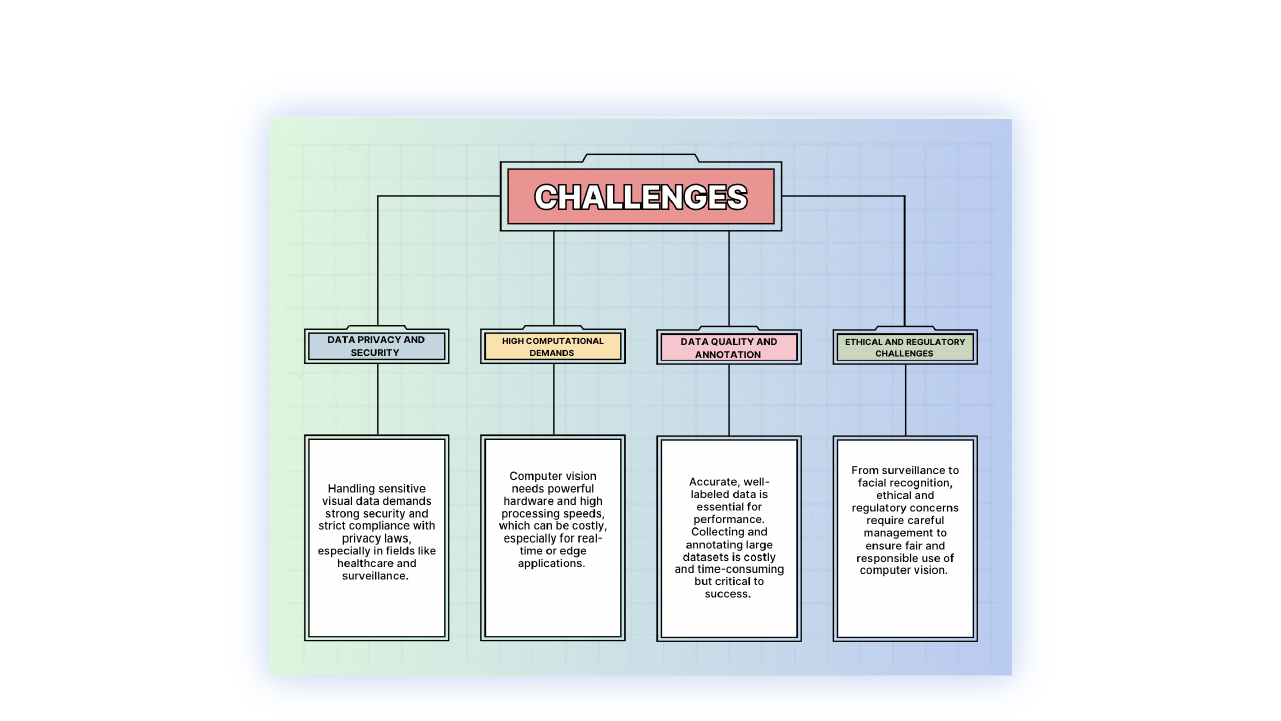
Challenges in Implementing Computer Vision
As with any technology, computer vision boasts some well-established advantages but also some challenges. But before diving into its applications, we must understand these hurdles to get the most out of its practical use and limitations.
Applications of Computer Vision
This part will show how computer vision is utilised in various domains.
Manufacturing
- Productivity Analytics: Visual data is used to analyze assembly line efficiency, monitor bottlenecks as they occur and maximize worker productivity. Facts obtained from real-time analysis help manufacturers adjust and minimize downtime and streamline flow processes.
- Visual Inspection of Equipment: This real-time inspection detects defects, wear, or potential equipment failures. Visual inspections are performed automatically, reducing human error, reducing the time for proactive maintenance and decreasing production delays.
- Quality Management: Check products for defects, shape, colour, or texture inaccuracies to ensure each item meets quality standards. This will increase the speed of doing quality checks and reduce the need for manual inspection.
- Skill Training: This type of training offers visual guidance and feedback to workers on tasks, allowing them to learn complex procedures more quickly. Video analysis can prove that a worker adhered to best practices.
Healthcare
- Cancer Detection: Computer vision is used to spot early signs of cancer in medical images, such as MRI and CT scans. It decreases errors, decreases the amount of time associated with diagnosis, and speeds up disease identification.
- COVID-19 Diagnosis: It helps healthcare professionals by processing lung images to detect COVID-19-related abnormalities with higher precision, which helps in diagnosing and monitoring disease.
- Cell Classification: It helps differentiate cell types in biological samples used for research and diagnostics. This tool’s ability to speed up biomedical research and open the way for personalized medicine makes it a very useful research tool.
- Movement Analysis: The device tracks a patient’s movements for rehabilitation or physical therapy and provides positive feedback on gait, posture, and movement patterns to aid in recovery.
- Mask Detection improves compliance with mandated masking in healthcare facilities, prevents face coverings, and better protects patients and staff by identifying those without face coverings. Tumour detection speeds up scans so that radiologists can spot potential tumours and get through scans more quickly, finding more tumours.
- Disease Progression Score: It helps physicians monitor and change treatments as they track the time progression of diseases by analyzing changes in medical images.
- Healthcare and Rehabilitation: They monitor patients’ physical progress during therapy to ensure they do prescribed exercises and do not injure themselves further.
- Medical Skill Training: It helps trainees improve their surgical skills in real-time by analyzing their techniques and providing real-time feedback.
Agriculture
- Animal Monitoring: Visual monitoring of health, location, and behaviour helps us detect signs of illness in livestock earlier and optimize animal welfare.
- Farm Automation: It helps with autonomous farming equipment such as tractors and drones, i.e., machines that can accurately complete work like planting, harvesting, and spraying to deliver high efficiency and minimize labour costs.
- Crop Monitoring allows farmers to make data-driven decisions on how to improve yields, determining plant health and growth stage, pest infestations, and soil condition.
Transportation
- Traffic Flow Analysis monitors traffic conditions in real time, detects congestion, and optimizes traffic light timings to ensure a safer road and reduced travel times.
- License Plate Recognition: The identity of a vehicle’s license plate is automatically identified for toll payments, parking management, and law enforcement applications.
- Autonomous Vehicles: The more powerful self-driving cars can detect objects, pedestrians, and other vehicles on the road and allow safe navigation.
- Driver Monitoring: It monitors driver fatigue and distraction levels and notifies drivers to avoid accidents caused by tunnelling or distraction.
- Railway Track Inspection: It detects the need for maintenance on railway tracks by analyzing them for wear, cracks, and other problems to increase safety by identifying them early.
Sports
- Athlete Performance Analysis: It analyzes the athlete’s speed, movements, and technique to optimize performance, prevent injuries, and provide personalized training programs.
- Game Strategy Development uses game footage to study player formations, strategies, and tactics and to improve team strategy.
- Fan Engagement: This adds value to the fan experience with multiple types of interactive real-time stats and replays and personalized content in real-time of live games.
Retail
- Customer Behavior Analysis collects customer data, such as when and where they’ve shopped, to encourage a better shopping pattern, layout, and marketing strategies.
- Inventory Management: It automates stock monitoring, alerting staff when reels or shelves require replenishment or have gone missing, reducing manual checks and avoiding stock outs.
- Checkout Automation: This helps a cashier-less checkout solution detect as customers leave, offering convenience and decreasing the waiting time.
Security
- Surveillance Systems Monitor areas with real-time video feeds, detect suspicious activities and make areas safer in public and private spaces.
- Intrusion Detection: It notifies security personnel about unauthorized access to restricted zones, sending real-time data to improve response times.
- Access Control: It verifies identities using face recognition or any other biometric method to enable secure entry to sensitive places.
Construction
- Site Monitoring: Sits over construction sites to monitor project progress, worker activity and compliance with safety.
- Safety Compliance: It helps prevent the wearing of necessary protective gear, like helmets and vests, and detects if workers are wearing them.
- Progress Tracking: It captures daily site data to compare to project timelines, ensure they’re being met, and recognize any delays.
Smart Cities
- Public Safety: It assists in boosting urban safety by monitoring activities or emergencies that have become unusual and automatically notifying people.
- Traffic Management: From real-time data, it optimizes traffic flows to reduce congestion and pollution in urban areas.
- Waste Management: It observes waste levels in public bins and manages a collection schedule to prevent the bins from overflowing while keeping them clean.
Environmental Monitoring
- Wildlife Conservation: Analysis tracks animal populations, migration patterns and behaviour to help pursue conservation goals.
- Pollution Detection enables the identification of air, water, and soil pollution sources and pilgrimages and the control of environmental influence.
- Disaster Management includes monitoring and collecting real-time data during natural disasters to support evacuation and relief operations.
Entertainment
- Content Creation: Enhanced treatment of visual effects and animation, making it easier to produce more quickly and under more dynamic conditions.
- Audience Analysis: But it’s a metric of viewer reaction and engagement, which allows creators to adjust their content accordingly.
- Virtual Reality: Since it creates an immersive experience for users, it offers games, simulations and training programs with a much better experience.
Education
- E-Learning: Provides interactive, visually rich online learning platform support.
- Classroom Monitoring: The tool tracks student behaviour and attention, and educators use it to improve their teaching skills.
- Student Engagement: Adapts learning materials to the student’s needs by analyzing student participation.
Finance
- Document Verification: ID and financial document audits will be automated, reducing the number of days to join and improving security.
- Fraud Detection: This also helps it identify unusual patterns and anomalies and prevent fraudulent activity.
- Customer Service: This is banking fused with personal and secure.
Real Estate
- Property Valuation: It makes appraisals based on accurate visual data.
- Virtual Tours: Virtual 3D tours allow offers to potential buyers to view properties without real-life handsets.
- Facility Management: It monitors building conditions to optimize maintenance schedules and minimize operating costs.
Energy
- Infrastructure Inspection: Power lines, pipelines, and other infrastructure are inspected to reduce manual inspection and improve safety.
- Leak Detection: It detects leaks in gas pipelines and other facilities to prevent accidents and reduce waste.
- Resource Management: It helps to analyze resource use to reduce consumption and optimize the operation.
Logistics
- Package Tracking: Monitors the journey of shipments in real-time, improving reliability and transparency.
- Route Optimization: Suggests efficient delivery routes, reducing fuel costs and delivery times.
- Warehouse Management: Automates inventory tracking and management within warehouses, streamlining operations.
Telecommunications
- Network Monitoring: It also ensures the network is reliable by watching for infrastructure disruptions or anomalies
- Infrastructure Maintenance: These preventative actions inhibit telecom tower and equipment maintenance and, as a result, prevent service interruptions.
- Customer Experience: Study the feedback given by the customer to improve the quality of the service.
Legal
- Document Analysis: The review of legal documents becomes automated, saving time while eliminating manual errors.
- Evidence Review: It analyses the visual evidence for case preparation and court proceedings.
- Compliance Monitoring: This involves monitoring some procedures and the documents that reflect them to ensure they are procedurally, legally, and regulatory compliant.
Hospitality
- Guest Recognition: Uses face recognition for personalized services and smoother check-in experiences.
- Service Personalization: Tailor’s services are based on guest preferences and behaviour, enhancing satisfaction.
- Facility Management: Monitors facility conditions, ensuring timely maintenance and enhancing guest comfort.
Aviation
- Aircraft Inspection: Inspections of aircraft for defects that require maintenance are conducted by the observer.
- Baggage Handling: Tracking baggage through the airport lowers the likelihood of lost baggage and is efficient in airports.
- Passenger Experience: Cheaper check-in and more personalized services.
Autonomous Solutions with Computer Vision
Apart from the above, there are 100 other applications for which we can use computer vision, which eventually become the building blocks for different autonomous solutions; let’s see a few of them.
Autonomous Retail Store: Computer vision is the bedrock of an autonomous retail store and drives a continuous shopping journey. Customers can walk in, choose items off the shelves and go. As the customer adds items to the cart, cameras and sensors record each item, and the system automatically charges the customer upon exiting. And this touch-free, effortless shopping is an easy on-the-go grab for essentials. In computer vision, the stock levels are managed in real-time – whether the staff needs to be alerted for restocking – so the users can always find them without interference or delay.
Autonomous Liquor Shop: Autonomous liquor stores bring security and convenience with computer vision. Facial recognition or ID scanning is used during age verification to ensure products can be accessed without slowing down the experience, as a degree of compliance is required. At checkout, items are automatically charged, and purchases are instantly tracked using computer vision. The system keeps strict control and does not allow unauthorized access while users can browse freely. This solution also handles inventory precisely to ensure that staff are alerted when stocking a particular item gets low so that users always have access to their favourite brands without waiting.
Autonomous Pharmacy: An autonomous pharmacy is an app with computer vision as its backbone, which allows patients to quickly and securely access their medications. The system records the items; users enter and select what they need and auto-pay–no assistance is involved. The solution verifies identity in a breeze for prescriptions, allowing users to get the right medicine securely. The computer vision program continuously tracks stock levels, ensuring that essential supplies are ready whenever the customer demands them to provide a well-stocked, convenient and convenient pharmacy at the customer’s home with which he or she can count on being secure and personalized.



