Introduction
In the rapidly evolving digital age, the concept of autonomous agents — software entities that perform tasks without human intervention has gained significant attention. These agents are increasingly becoming invaluable tools for creators across various domains, from content creation to marketing and beyond. This blog explores how autonomous agents are revolutionizing the creative landscape, providing detailed insights into their applications, benefits, and future potential.
Traditional AI models, while impressive, often require constant guidance, similar to interns in a workplace. However, the emergence of autonomous AI agents introduces a groundbreaking paradigm in which these intelligent entities can operate independently without manual intervention. Autonomous AI agents are programs or entities capable of perceiving their environment, making decisions, and achieving specific goals without human intervention. They can mimic or simulate human intelligence in particular domains or tasks.
Autonomous agents are systems designed to perform specific tasks independently, using artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms. They come in various forms, including chatbots, virtual assistants, and content-generation tools.
Applications of Autonomous Agents for Creators
1. Content Creation
Autonomous agents are increasingly used in generating written, visual, and audio content. Tools like OpenAI’s GPT-4 can produce high-quality articles, scripts, and social media posts based on a set of prompts. Visual content creators utilize AI tools like DALL-E to generate images from textual descriptions, while musicians use AI to compose and produce music.
- Writing and Editing: Autonomous writing tools can draft articles, create blog posts, and even write books. They can also assist in editing by checking grammar, style, and coherence, significantly reducing the time spent on these tasks.
- Graphic Design: AI-driven design tools can create logos, banners, and other visual assets. They can suggest design elements based on current trends and the creator’s brand identity.
- Music and Sound: AI tools can compose original music, suggest chord progressions, and even produce complete tracks. These tools analyze existing music to create compositions that align with specific genres or moods.
2. Social Media Management
Managing social media accounts can be time-consuming. Autonomous agents can schedule posts, analyze engagement metrics, and even respond to comments and messages. This automation allows creators to maintain a consistent online presence without being tied to their devices.
- Content Scheduling: Tools like Buffer and Hootsuite use AI to determine the best times to post content for maximum engagement.
- Analytics and Insights: Autonomous agents can analyze social media performance, providing insights into what content resonates most with the audience.
- Customer Engagement: Chatbots can handle routine inquiries and interact with followers, providing immediate responses and freeing up creators’ time for more critical tasks.
3. Marketing and Promotion
Autonomous agents can enhance marketing campaigns by analyzing extensive data and making data-informed decisions. They can help identify target audiences, personalize marketing messages, and track campaign performance.
- Ad Campaign Optimization: AI-driven platforms such as Google Ads and Facebook Ads utilize machine learning to optimize ad placements and budgets, thereby ensuring that creators receive the best return on investment.
- Email Marketing: Tools like Mailchimp use AI to segment audiences, personalize email content, and predict the best times to send emails for maximum open rates.
- Market Research: Autonomous agents can analyze market trends, competitor activities, and consumer behavior, providing creators with valuable insights to refine their strategies.
Components of Autonomous Agent
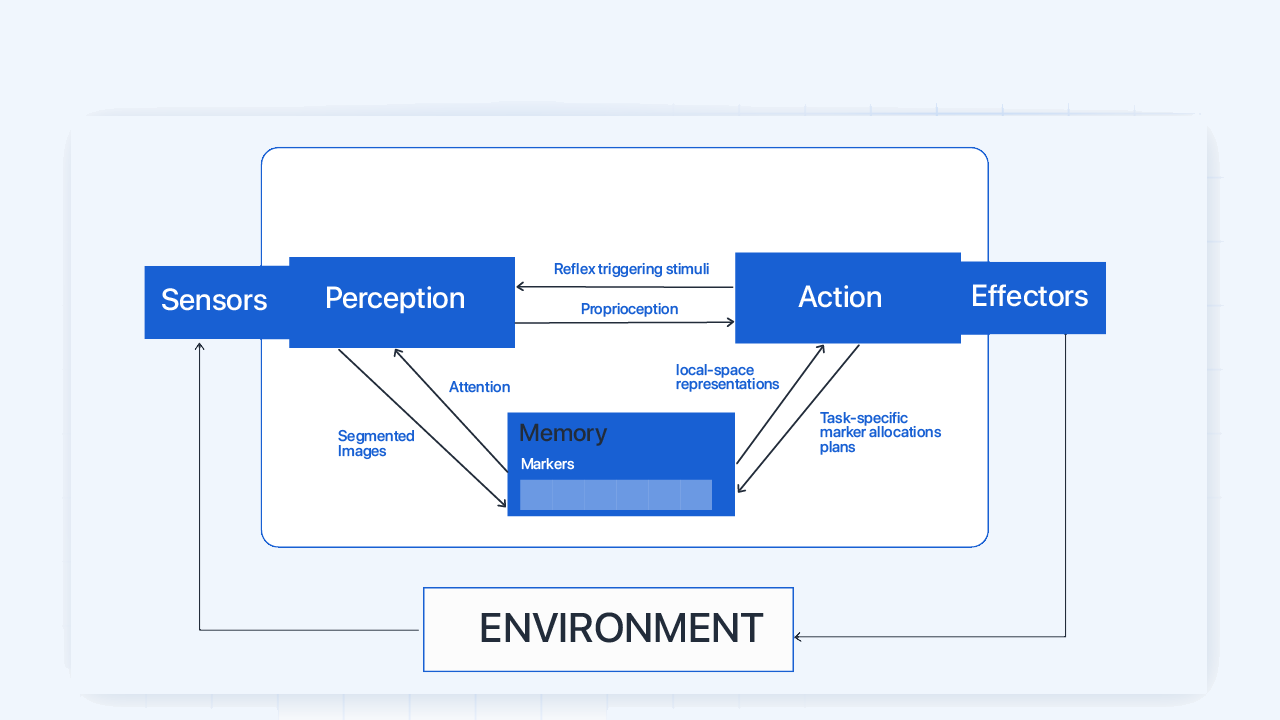
Below, we summarize components that work together or independently to attain a defined goal while allowing users maximum autonomy.
1. Sensors
In the use cases of creators, sensors could be tools that gather data about the creative process, such as:
- Time tracking software to monitor how much time is spent on a project
- Keyboard and mouse tracking to analyze workflow and productivity
- Social media APIs gather data on audience engagement and feedback.
This data is used to inform the agent’s decision-making process and provide insights to the creator.
2. Perception
Perception involves interpreting the data gathered by the sensors to understand the current state of the creative project. This includes:
- Analyzing time-tracking data to identify patterns and areas for improvement
- Using machine learning(ML) algorithms to identify trends in audience engagement and feedback
- Identifying areas of the project that require more attention or resources
The perceived state of the project is used to inform the agent’s reasoning and decision-making processes.
3. Reasoning
Reasoning involves using the perceived state of the project to make decisions about what actions to take. This includes:
- Identifying areas of the project that require more attention or resources
- Suggesting changes to the workflow or creative process to improve productivity
- Providing recommendations for new tools or software to improve the creative process.
The reasoning process is used to generate a set of possible actions for the agent to take.
4. Action Selection
Action selection involves choosing the best action to take based on the reasoning process. This includes:
- Suggesting a new workflow or creative process to improve productivity
- Providing recommendations for new tools or software to improve the creative process
- Identifying areas of the project that require more attention or resources
The selected action is then carried out by the agent.
5. Actuators
Actuators are the components that carry out the selected actions. In the context of creators, actuators include:
- Software tools that automate repetitive tasks or provide new functionality
- APIs that integrate with existing tools and software to provide new features
- Human assistants provide support and guidance to the creator.
The actuators carry out the selected actions to improve the creative process and provide support to the creator.
6. Goal Representation
Goal representation involves defining the objectives of the creator and the agent. This includes:
- Improving productivity and efficiency
- Enhancing creativity and innovation
- Providing better support and guidance to the creator
The goal representation is used to inform the agent’s decision-making process and ensure that the agent is working towards the creator’s goals.
7. Planning
Planning involves generating a sequence of actions to achieve the creator’s goals. This includes:
- Developing a project plan and timeline
- Identifying key milestones and deadlines
- Providing recommendations for new tools or software to improve the creative process.
The planning process is used to generate a roadmap for the agent to follow and ensure that the creator’s goals are achieved.
8. Human-Agent Interface
The human-agent interface involves providing a way for the creator to interact with the agent. This could include:
- A user-friendly interface for accessing the agent’s insights and recommendations
- A system for providing feedback and guidance to the agent
- A way for the creator to customize the agent’s behavior and goals
Example
- Sensors: The agent uses time-tracking software and keyboard and mouse tracking to gather data on the designer’s workflow and productivity.
- Perception: The agent analyzes the data to identify patterns and areas for improvement, such as identifying tasks that take up the most time or identifying areas of the design that require more attention.
- Reasoning: The agent uses the perceived state of the project to make decisions about what actions to take, such as suggesting changes to the workflow or providing recommendations for new design tools.
- Action Selection: The agent selects the best action to take, such as suggesting a new workflow or providing recommendations for new design tools.
To build autonomous agents, we need to ultimately mimic human thinking patterns and proactively plan for task execution. During planning, we can create LLM agents and break down large and complex tasks into smaller, manageable steps. These agents must be able to learn from their past actions and track successful results against mistakes. This data helps the overarching autonomous agent to optimize its future steps and improve results.
Benefits for Creators
- Innovation and Creativity: Generative AI opens new avenues for creativity by providing tools that can generate ideas and content that might not have been conceived by human creators alone. This collaboration between human intuition and artificial intelligence can lead to groundbreaking innovations in art, music, writing, and more.
- Time and Cost Efficiency: By automating routine tasks and accelerating the content creation process, autonomous agents and generative AI significantly reduce the time and cost associated with creative projects. This efficiency allows creators to take on more projects and explore new creative directions without being bogged down by repetitive work.
- Enhanced Quality: AI-powered tools can enhance the quality of creative outputs by providing insights and suggestions that might be overlooked by human creators. For example, AI-driven editing tools can improve the coherence, style, and impact of written content, while generative design tools can optimize visual compositions for aesthetics and functionality.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity: Generative AI and autonomous agents democratize creativity by making advanced tools accessible to a wider audience. Novices and hobbyists can leverage these technologies to produce professional-quality work without requiring extensive training or resources. This inclusivity fosters a more diverse and vibrant creative community.
Conclusion
Autonomous agents and generative AI represent a transformative force in the creative industry, offering unprecedented opportunities for innovation, efficiency, and accessibility. By embracing these technologies, creators can push the boundaries of their craft, explore new possibilities, and deliver high-quality content with greater ease and impact. As these technologies continue to evolve, their integration into the creative process will undoubtedly become even more profound, shaping the future of creativity in ways we can only begin to imagine.



