Introducing Google Security Services
Data Security is a primary design consideration for all of Google’s infrastructure, products, and personnel operations. The collaboration of Google with the security research community enables them to address vulnerabilities quickly or prevent them entirely. Google Security Services is indeed required to secure GCP and other google services.
Organizations have typically turned to the public cloud for cost reductions or increased private data centers’ ability. However, organizations are now looking for security primarily at the public cloud, realizing that Cloud Service providers deliver secure infrastructure. It was thus helping them invest more in people and processes.
Key Components of Google Security Services
Zero Trust Security Model: The Zero Trust Security Model ensures that no entity, internal or external, is trusted by default. All access requests are authenticated and authorized, reducing the risk of breaches. Google implements this with real-time data analysis and continuous monitoring, making it a core component of Google Cloud’s security.
Compliance and Regulatory Standards: Google Cloud offers tools to help businesses meet compliance requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2. These built-in features support organizations in maintaining regulatory standards while ensuring data privacy and integrity.
Incident Response and Recovery: Google Cloud provides advanced tools for detecting, responding to, and recovering from security incidents. With real-time monitoring and automated response workflows, businesses can minimize the impact of security breaches and improve recovery times.
Advanced Threat Detection: Google employs machine learning and behavior analytics for advanced threat detection, identifying risks like unauthorized access and vulnerabilities early. Tools like Chronicle and Security Command Center help proactively mitigate threats across the cloud environment.
User Education and Awareness: Google provides training and resources to educate employees on security best practices, reducing the risk of phishing, social engineering, and other common cyber threats. Building a strong security culture is a critical part of Google Cloud’s approach.
Google Infrastructure Security Layers
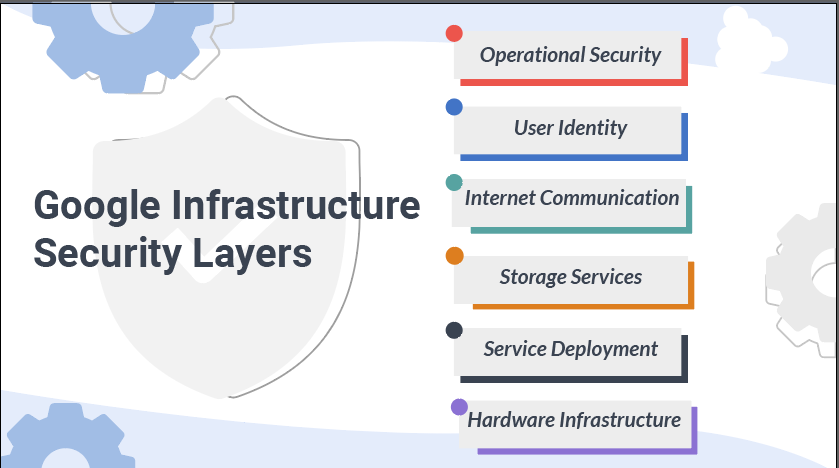
We will now discuss the Google Infrastructure Security Layers, which supports both the enterprise and the consumer. Enterprise services include GSuite and Google Cloud Platform.
Secure Low-Level Infrastructure
We explain how we protect the lowest levels of our networks within this segment, from the physical premises to the purpose-built hardware within the data centers to the low-level software stack operating on any device.
- Security of Physical Premises: Google uses multiple physical security layers to protect data center floors and use technologies like biometric identification, metal detection, cameras, vehicle barriers, and laser-based intrusion detection systems.
- Hardware Design and Provenance: A data center for Google consists of many server machines connected to a local network. Google custom-designs the server boards and the networking equipment.
- Secure Boot Stack and Machine Identity: Google server machines use various technologies like BIOS, bootloader, kernel, and base operating system image to ensure the correct software stack booting.
Secure Service Deployment
Let us describe how the hardware and software help to ensure that a service is deployed securely on our infrastructure.
- Service Identity, Integrity, and Isolation: For inter-service communication, google uses cryptography authentication and authorization at the application layer. This provides robust and abstraction-level access control and granularity that administrators and services naturally understand.
- Inter-Service Access Management: The owner of a service can use the infrastructure’s access management features to specify precisely which other services can communicate with it.
Secure Data Storage
Google implements secure data storage on the infrastructure.
- Encryption at Rest: Google’s infrastructure provides a wide range of storage services, including Bigtable and Spanner, as well as an essential management service.
- Deletion of Data: Deleting Google data most often starts with marking specific data as “deletion scheduled” rather than deleting the data.
Secure Internet Communication
Google isolates infrastructure from the Internet into a private IP space. Additional security such as the denial of service defenses (DoS) threats can be enforced more effectively by directly exposing a subset of machines specifically to external internet traffic.
- Google Front End Service: If a service intends to be made available on the Internet, it can register itself with the Google Front End (GFE) infrastructure service.
- Denial of Service (DoS) Protection: Google’s overwhelming scale of infrastructure allows Google to handle loads of DoS threats easily. Google has multi-tier, multi-layer DoS safeguards that further reduce the risk of any DoS effect on a GFE operation.
- User Authentication: The next layer of defense after DoS protection comes from google’s central identity service. This service usually manifests to end users as the Google login page.
Operational Security
Last but not least, google operates the infrastructure securely from their employees’ machines and credentials. Google defends against threats to the infrastructure from both insiders and external actors.
- Safe Software Development: Google has a high emphasis on the secure environment for development; thus, it uses manual security reviews and in-depth design and implementation reviews for the riskiest features.
- Keeping Employee Devices and Credentials Safe: Google makes a considerable investment to protect their employees’ equipment and credentials from compromise and monitor activities to identify potential compromises or illicit insider activity.
Securing Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
This section lets us determine how GCP, a public cloud infrastructure, benefits from underlying infrastructure security. To better understand the infrastructure and how it provides service-specific security improvements that we build on top of the infrastructure to GCP, let’s take the example of Google Compute Engine. Compute Engine allows customers to run their virtual machines on the infrastructure of Google. The compute Engine consists of the management control plane and the virtual machines. Let’s go-ahead to know more.
- The Compute Engine control plane exposes its API via the GFE, leveraging infrastructure security features such as Denial of Service (DoS) protection and centrally managed support for SSL / TLS.
- End-user authentication to the Compute Engine control plane API is performed through Google’s centralized identity service, providing security features such as hijacking detection. Authorization is done using the central IAM service in the cloud.
- The network traffic for the control plane, from the GFEs to the first service behind it and from other control plane networks, is properly authenticated and protected by the system. It passes from one data center to another.
- Compute Engine persistent disks are encrypted at-rest using keys protected by the central infrastructure’s key management system.
- The isolation provided to the VMs is based on hardware virtualization using the open-source Kernel-based Virtual Machine Stack.
- Compute Engine’s use of customer data obey the GCP use of customer data policy. Google does not access or use customer data, except when required to provide services to customers.
Google Security Checklist
- Enable 2-Step Verification: Activate 2-Step Verification for all admin accounts and users to enhance security.
- Avoid Super Admin Accounts for Daily Tasks: Use non-admin accounts for daily activities and sign out of super admin accounts when idle.
- Set Up Email Alerts for Admin Activities: Configure email alerts for admin actions and regularly review audit logs for unusual activity.
- Add Recovery Options to Admin Accounts: Set up recovery options (spare security keys, backup codes) for quick recovery of admin accounts.
- Use Unique Passwords and Enforce Alerts: Ensure unique passwords for each account and enable password reuse alerts.
- Review Activity Reports and Alerts Regularly: Monitor activity reports and alerts to detect any suspicious behavior.
- Limit Third-Party App Access and Whitelist Trusted Apps: Control third-party app access to GSuite and create a whitelist of trusted apps.
- Configure Email Security: Ensure SPF, DKIM, and DMARC validation, disable automatic forwarding, and enable pre-delivery message scanning.
- Restrict Group Creation to Admins: Limit group creation to admins and ensure private access to groups.
- Enforce Mobile Security: Require passwords on mobile devices, enable encryption, inactivity reports, and disable access to offline docs.
- Limit Calendar Sharing: Restrict external calendar sharing and prevent automatic contact info sharing.
- Control Chrome policies: Implement Chrome policies and warn users about unapproved add-ons or external chats.
Use Cases for Google Security Services
1. Healthcare Data Protection and Compliance (HIPAA): A leading healthcare provider used Google Cloud’s security services to meet HIPAA regulations. By leveraging Google Cloud’s data encryption and access management tools, they ensured secure storage and transfer of patient data while maintaining compliance with strict healthcare regulations.
2. Financial Services and Fraud Detection: A major financial institution implemented Google Cloud’s Zero Trust security model and AI-driven threat detection to enhance fraud detection systems and safeguard sensitive customer data. Google’s Security Command Center helped monitor activities and detect anomalies in real-time.
3. Government Agencies and Data Sovereignty: Government organizations used Google Cloud’s compliance certifications (such as FedRAMP and CJIS) to meet regulatory requirements for data storage and access. They leveraged data residency options and advanced encryption to protect sensitive national security information.
4. Retail and E-Commerce Security: Large e-commerce companies turned to Google Security Services to safeguard customer data, improve transaction security, and prevent cyberattacks. Using Google Cloud’s DDoS protection, network security, and data encryption ensured compliance with PCI DSS while enhancing the customer experience.
5. Manufacturing and IoT Security: A manufacturing company used Google Cloud’s security tools to secure their IoT devices and ensure the integrity of their industrial control systems. Google’s advanced threat detection and incident response tools helped mitigate risks of cyberattacks targeting their connected devices and infrastructure.
Future Trends in Google Security Services
- AI and Machine Learning for Threat Detection: Google is integrating AI and machine learning to enable real-time threat detection, anomaly detection, and predictive analytics, allowing faster identification of threats compared to traditional methods.
- Zero Trust Security Model: The Zero Trust model is gaining traction in Google Cloud, ensuring that all users and devices are verified before access is granted. This is supported by Identity and Access Management (IAM) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) for stronger security.
- Quantum-Resistant Cryptography: As quantum computing advances, Google is developing quantum-safe encryption algorithms to protect data from future quantum threats, ensuring long-term security.
- Serverless and Container Security: With the rise of serverless computing and containers, Google is enhancing security tools to protect these dynamic environments from vulnerabilities and attacks.
- Cloud-Native Security and Automation: Google Cloud is automating security processes, such as vulnerability management and incident response, through tools like Security Command Center and Chronicle, enabling quicker threat responses and reducing human error.
- Privacy and Compliance as a Service: Google continues to improve its compliance tools to help businesses meet global privacy regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA, offering features like audit trails, data residency, and automated compliance reporting.
Best Practices for Organizations
To make the most of Google’s security features, organizations should adhere to these best practices:
- Implement the Zero Trust Model: Trust no one by default and always verify user and device identities before granting access.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits: Use Google Cloud’s built-in auditing and logging features to monitor access and activities within your environment.
- Leverage Encryption: Ensure all sensitive data is encrypted both in transit and at rest using Google’s encryption features.
- Stay Compliant: Use Google’s tools to monitor and maintain compliance with relevant industry regulations.
- Educate Employees: Provide ongoing security training and awareness programs to ensure your team understands how to recognize and respond to potential threats.
Core Google Security Takeaways
Google Security Services are essential for enterprises using Google Cloud Platform (GCP) and other Google services. These services offer data encryption, access management, and real-time threat detection to ensure security and regulatory compliance. Whether securing customer data or cloud infrastructure, Google provides the necessary tools to mitigate risks. Additionally, we offer insights into AWS Security Services for those exploring alternative solutions. Remember, “We Never Stop at Success, We Go Ahead”, continuously improving our security offerings to meet the evolving needs of businesses.