Introduction of GenAI and Amazon Q
In the ever-changing realm of cybersecurity, cyber threats are becoming complex and widespread. Generative AI solutions such as Amazon Q have emerged as promising assets in the battle against cyber threats. These technologies can transform cybersecurity practices, providing methods to identify and prevent risks.
Generative AI is a form of AI that can generate original content and concepts across various mediums, such as conversations, stories, images, videos, and music. In today’s era, there are numerous instances of generative AI, such as ChatGPT and Bard. Organizations can utilize generative AI for a variety of purposes, including chatbots, media production, and product development and design.
Amazon has unveiled its very own Gen AI assistant known as Amazon Q. What distinguishes Amazon Q from ChatGPT and Bard is its distinctive architecture. Amazon Q is not constructed on a specific AI model. Instead, it utilizes the Amazon Bedrock platform, which links various AI systems including Amazon’s Titan and models developed by Anthropic and Meta. This approach enables Amazon Q to take advantage of a blend of AI technologies, thereby enhancing its capabilities.
It is designed to understand employees’ roles and permissions and provides personalized interactions so that “no one can access data that they’re not authorized to”.
Use cases of Amazon Q
Amazon Q is a tool designed for deriving insights from a dataset, not simply a general-purpose tool like GPT. Companies can grant permission for it to interact with their corporate data.
- Data Analysis: Amazon Q can analyze large sets of data and provide summaries or insights, making it easier to understand complex data patterns.
- Automated Customer Support: It can be used to handle customer inquiries automatically, providing quick and accurate responses to common questions.
- Generating Business Insights: By accessing company data, Amazon Q can generate insights and recommendations to inform business strategies.
AI for Threat Detection and Response
Artificial intelligence enhances cybersecurity by analyzing network traffic and user behavior to proactively identify potential threats, enabling organizations to prevent attacks. Some capabilities of AI that empower cybersecurity are Adaptive learning, Advanced pattern recognition, Automated responses, and Predictive analytics.
Generative AI stack for Threat Detection
Consider the diagram below for the “Generative AI stack” as designed by AWS for Amazon Q, which can be utilized in applications like threat detection.
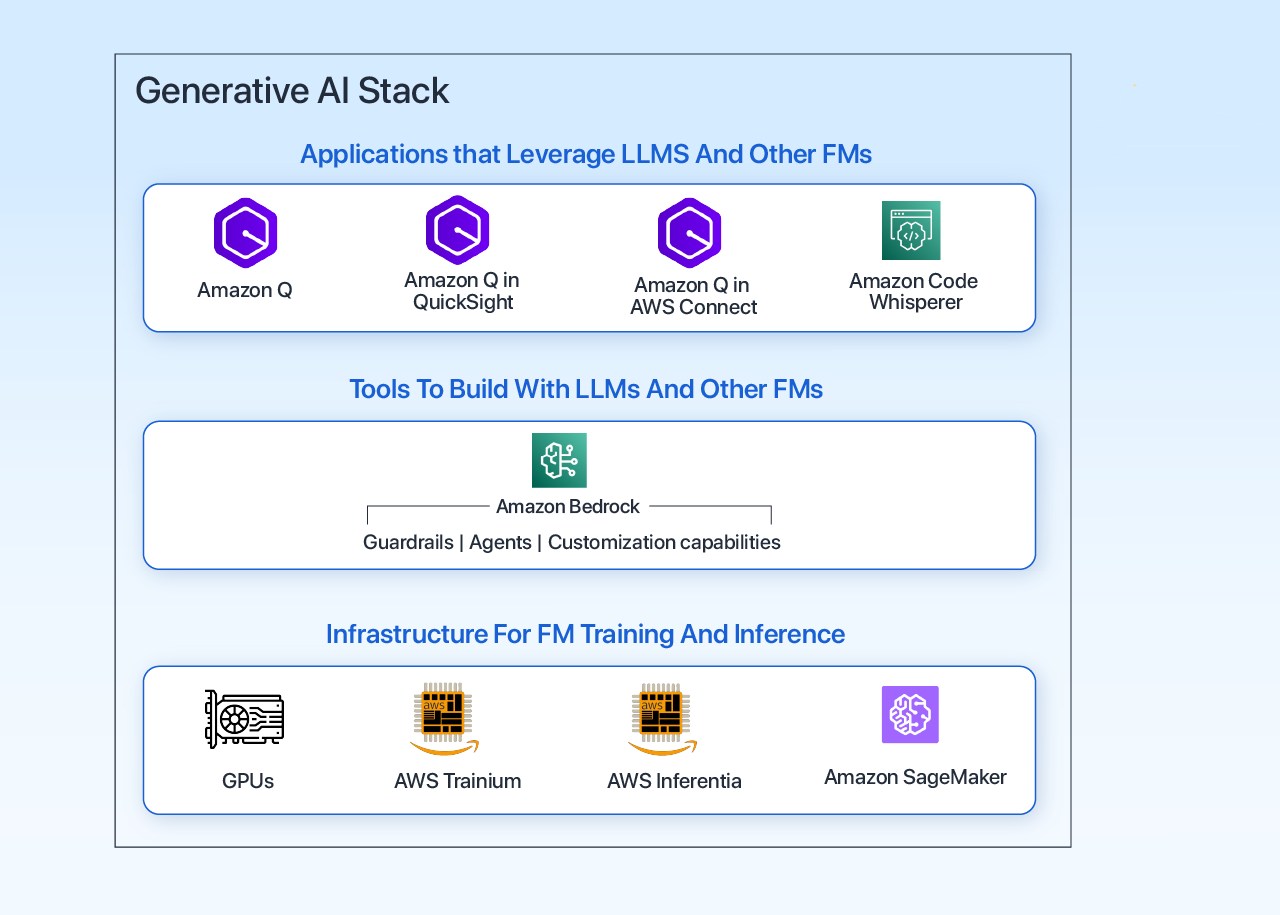
Brief Description
The image depicts a “Generative AI stack” by AWS for Amazon Q, which can be utilized for the maintenance of advanced threat detection systems using generative AI and other foundational models.
- Applications Utilizing LLMs: These AWS services and tools facilitate the integration and application of LLMs in diverse computational contexts.
- Tools for Developing with LLMs and Other FMs: Amazon Bedrock provides essential support for developers creating applications that utilize LLMs within AWS environments.
- Infrastructure for FM Training and Inference: AWS GPUs, Trainium, and Inferentia deliver robust infrastructure for the efficient training and inference of ML models.
Securing Data with Immutable Ledgers
An Immutable ledger is a database that is entirely distributed and decentralized. It documents transactions and data chronologically and unalterably.
Immutability signifies the incapacity to modify or delete any data once it has been logged onto the ledger. This happens through cryptographic methods and agreement mechanisms that render it impossible to change historical data.
Data Security using Immutable ledgers and Amazon Q
Immutable ledgers are employed to make data security easier and stronger, particularly in relation to blockchains. Here’s how Amazon Q enhances data security using immutable ledgers.
- Transparency and Accountability: Organizations can maintain a transparent record of transactions and actions helping in identifying errors back to their source, promoting accountability.
- Data Security: Amazon Q, with immutable ledgers, ensures robust protection against tampering and unauthorized alterations.
- Smart contracts: Amazon Q’s, along with the ledger, extends capabilities to smart contracts — self-executing agreements that automate processes.
- Data Loss Resilience: Immutable ledgers distributed across a network of nodes are resilient to data loss, unlike traditional databases.
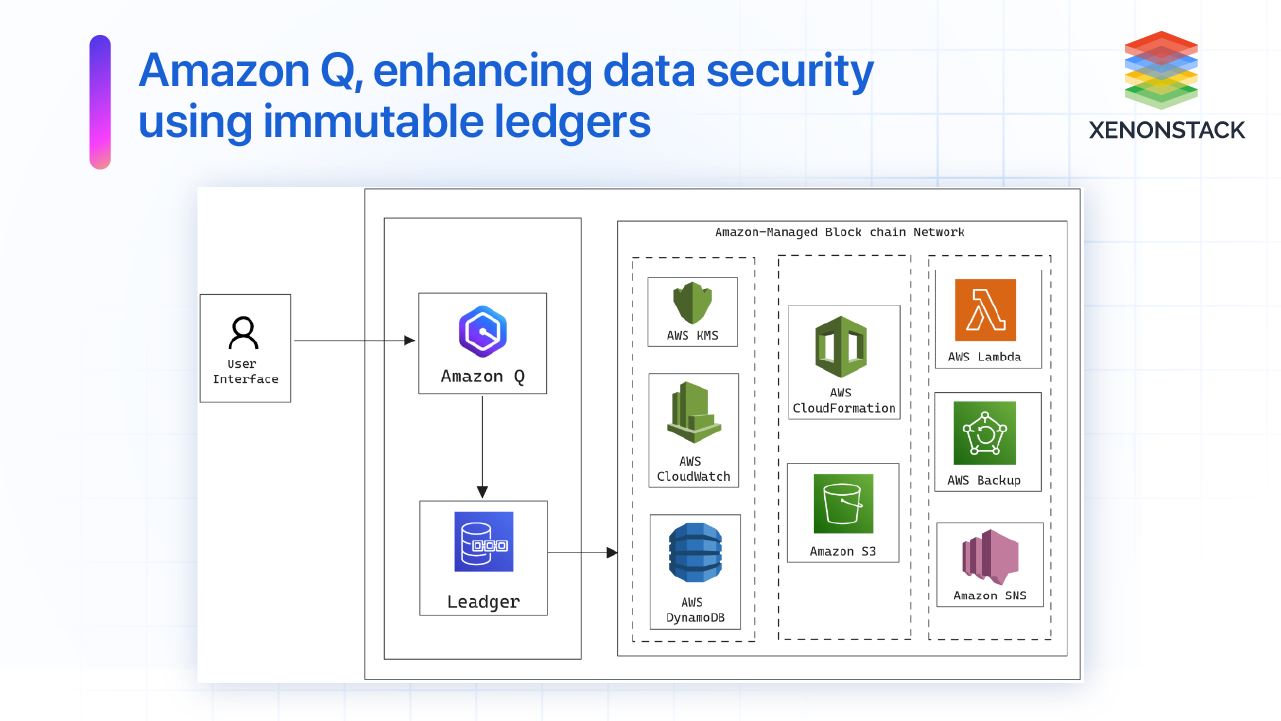
Brief Description
This architecture diagram demonstrates how Amazon Q, in conjunction with AWS services, enhances data security using immutable ledgers.
- Blockchain Integration: Amazon Q allows users to interact with the blockchain, it manages transactions, ensuring all data recorded is secure and immutable.
- Data Storage and Management: Amazon S3 is used to store data related to smart contracts and transaction logs. DynamoDB stores metadata for quick access and querying. AWS Backup ensures data reliability and recovery in case of data loss.
- Operational Tools and Automation: AWS Lambda automates the execution of smart contracts based on predefined triggers or events. AWS CloudFormation manages the deployment and updates of the entire infrastructure as code.
Automated Compliance and Auditing
AI significantly improves compliance audits by leveraging machine learning algorithms and data analytics, adding a higher level of complexity to the process.
- Data Analysis and Pattern Recognition: Amazon Q excels at handling large datasets, analyzing historical data, identifying patterns, and detecting anomalies.
- Automation of Routine Tasks: AI can automate routine and repetitive audit tasks effectively. Compliance professionals can focus on intricate aspects, while Amazon Q handles routine checks efficiently.
- Predictive Analytics for Risk Mitigation: AI’s predictive analytics capabilities help organizations identify potential compliance risks before they escalate.
- Customization for Industry-specific Compliance: AI solutions such as Amazon Q can be customized to meet industry-specific compliance requirements, such as those in healthcare, finance, etc.
Implementing Automated Compliance and Auditing
When incorporating AI into compliance audits, it is imperative for organizations to take a strategic approach.
- Data Integration: Ensure seamless integration of Amazon Q with existing data sources, enabling thorough data analysis and combining historical data with real-time insights.
- AI Training and Validation: Train AI algorithms using past compliance data, validate their accuracy, and continuously refine them to improve performance.
- Collaboration with Compliance Experts: Collaborating with compliance experts is crucial, human expertise ensures that the interpretation of results aligns with the intricacies of regulatory requirements.
Case Studies in Cybersecurity Enhancements
Let’s refer to these case studies, which depict the use of artificial intelligence to enhance cyber security.
IBM’s use of AI in CyberSecurity
Background: IBM, a well-known global leader in technology and consulting services, has adopted AI to detect and mitigate complex cyber threats.
Implementation: IBM has deployed Watson for Cyber Security, an AI platform that utilizes machine learning and natural language processing.
Results:
- Improved Threat Detection: Watson for Cyber Security has reduced incident investigation time by 60%. It processes data 50 times faster than human analysts, speeding up threat detection.
- Enhanced Accuracy: AI has increased the accuracy in identifying true positives. False positives have been reduced by 30%, enabling a more focused approach to real threats.
Microsoft’s use of AI for threat detection
Background: Microsoft, a prominent global technology company, has utilized AI to safeguard its cloud infrastructure and customer data.
Implementation: Microsoft has incorporated AI and machine learning algorithms into its security operations via the Microsoft Intelligent Security Graph, which analyzes over 6.5 trillion signals daily from its products and services.
Results:
- Swift Threat Detection and Response: Microsoft has reduced the average time to detect threats from 24 hours to less than an hour.
- Enhanced Threat Detection Rate: Microsoft’s AI-powered security solutions have increased the detection rate of malware and phishing attacks by 40%.
Future Trends in AI and Cybersecurity
It is crucial to comprehend emerging trends to harness AI’s potential effectively while managing risks.
- AI-Powered Threat Detection: AI’s ability to analyze large datasets in real-time significantly improves threat detection capabilities. Future advancements will concentrate on integrating AI into security operations to automate threat response.
- Adversarial AI and Defense: The emergence of adversarial AI calls for sophisticated defensive tactics. Strategies will progress to identify and counter AI-driven attacks, shaping the future of cybersecurity defenses.
- Ethical and Privacy Issues: Regulatory frameworks need to address these issues to ensure responsible deployment of AI.
Conclusion
The article delves into the integration of generative AI and Amazon Q within cybersecurity, exploring their multifaceted applications such as data analysis, customer support, and project management. It emphasizes how AI bolsters cybersecurity by improving threat detection, automating responses, and leveraging predictive analytics.
Additionally, the piece underscores the use of immutable ledgers to heighten security measures. Case studies featuring IBM and Microsoft illustrate AI’s role in cybersecurity, while the article forecasts upcoming trends in this field, highlighting ethical and privacy considerations.



