Frontier AI models are pushing the boundaries of artificial intelligence with advanced features like multi-modal processing, zero-shot learning, and scalable deployment. These models offer unmatched versatility and intelligence, but face challenges related to ethics, security, and resource-intensive deployment. Proper regulation, transparency, and safety measures are crucial to ensuring their responsible and effective use.
To stay competitive, businesses must adopt the latest technologies that drive innovation and efficiency. Frontier AI models are revolutionizing the way organizations approach complex challenges by offering unmatched versatility in processing text, images, and audio. These models enable businesses to adapt quickly, automate tasks, and make smarter, data-driven decisions. With the ability to handle multiple inputs simultaneously, frontier AI models are not just improving customer experiences, but also streamlining operations and boosting decision-making processes.
As these models continue to advance, their potential to transform business practices and drive success becomes more evident. This blog delves into how frontier AI Agents is redefining the future of business, unlocking new opportunities for growth, and empowering companies to stay ahead of the curve.
What Would Make an AI Model a “Frontier” Model?
The designation of a “frontier” model goes beyond mere computational power or parameter count. These models are distinguished by several key characteristics:
- Architectural Invention: Frontier AI models are characterized by complex neural network architecture, especially new attention mechanisms and how to use parameters efficiently. All these inventions make this model more effective in processing the information and lead to greater performance and responsiveness in any application.
- Performance Metrics: These models perform well on quite a few benchmarks and excel with capabilities in zero-shot as well as few-shot learning. Such generalization lets them adapt rapidly to new tasks with extremely minimal training, thus making it very versatile.
- Technical Competencies: Frontier models are ahead of other variants in multi-modal processing since they support both text, images, and audio inputs. Their advanced inference capabilities and contextual reasoning make them efficient on complex decision-making tasks, further expanding their scope across domains.
- Real-world Application: Frontier AI models are pretty flexible for use cases while coupled with strong error handling, that is reliable in the unpredictable environment. Scalable deployment options make them fit well to be integrated in other systems, thereby facilitating widespread adoption across industries.
Key Frontier Models in 2024
1. Claude 3 Family (Anthropic)
The Anthropic Claude 3 family includes three models, each of which is built for specific tasks.
- Claude 3.5 Sonnet (New) is the latest model, performing better in complex reasoning, analysis, and creative tasks, plus having the functionality of computer use (beta). It is highly precise and subtle, thus ideal for academic, technical, and creative applications.
- Claude 3 Opus specializes in elaborate writing, complex problem-solving, and shows proficiency in tasks that require careful analysis and extended reasoning.
- Claude 3 Haiku is optimized for speed and efficiency, delivering high-quality outputs in quick interactions, making it ideal for real-time tasks. Common features across this family include robust capabilities in code generation and analysis, nuanced understanding of context and instructions, and the ability to manage complex, multi-step tasks, all while incorporating built-in safeguards and ethical considerations.
2. Google Gemini
Google Gemini is available at Ultra, Pro, and Nano scale and is particularly known for mathematical reasoning as well as scientific analysis abilities. The model is very good at managing multi-turn conversations, holding context, and being tightly integrated with Google’s tools ecosystem.
It may address multiple knowledge domains at one time, thus being applicable to a variety of scenarios in enterprise as well as consumer applications. Its extensive training across diverse datasets ensures a comprehensive understanding of various contexts, enhancing its usability in complex scenarios.
3. GPT-4 Vision (OpenAI)
Advanced ability in analyzing and describing detail-rich images, OpenAI’s GPT-4 Vision is good at taking technical diagrams, charts, and graphs into consideration when visual contexts are complex. In a single conversation, this model can process numerous images, which enrich the interaction experience. GPT-4 Vision is suited to a variety of applications from generating educational content to creating documentation on technical topics, the tools for accessibility, the design review and feedback needed in many professional fields who have to interpret visual data.
- GPT-o1 Series (OpenAI): The GPT-o1 series by OpenAI specializes in reasoning capabilities-advanced mathematical reasoning, optimization, bug detection, and fixing. It provides strong support for logic building and documentation across multiple domains. Software architecture principles are good enough for this series to cohere well with the environments of development
4. LLAMA 3.2 (Meta)
Meta’s LLaMA 3.2 is optimized for edge computing in the sense that it should consume resources efficiently and minimize latency of processing as much as possible. Its mobile-first architecture is meant to make it run with ease on smartphone processors without being a battery hog; it supports seamless offline capability, making it suitable for applications where integration into mobile apps is desired, IoT devices, or real-time processing. This is especially in privacy-sensitive environments where local processing can be critical.
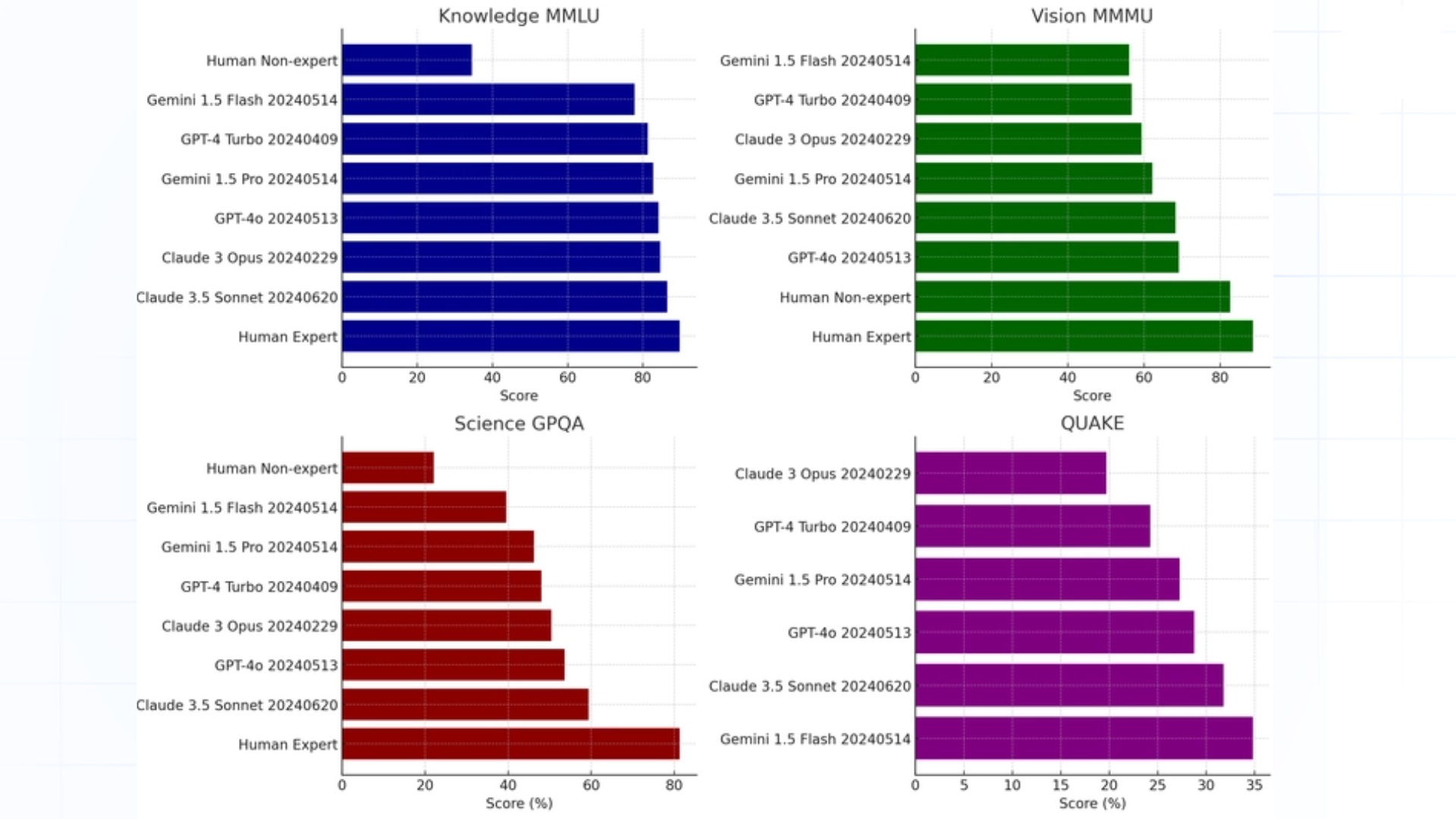
Overview of Recent Frontier Models
| Model | Graduate level reasoning (GPQA) | Undergraduate level knowledge (MMLU Pro) | Code | Math problem-solving (MATH) | Context window |
| Claude 3.5 Sonnet (new) | 65.0% | 78.0% | 93.7% | 78.3% | 200k |
| Claude 3.5 Haiku | 41.6% | 65.0% | 88.1% | 69.2% | 200k |
| GPT-4o | 53.6% | 72.55% | 90.2% | 76.6% | 128k |
| Gemini 1.5 Pro | 59.1% | 75.8% | — | 86.5% | 2M |
| GPT-o1-mini | 60% | 85.2% | 92.4% | 90% | 32k |
| LLama 3.2 70 B | 46.7% | 52.78% | – | 68% | 128k |
Characteristics of Frontier AI Models
- Multimodal Capabilities: Modern frontier models can process multiple data types simultaneously. For example, GPT-4 Vision can process text and image inputs simultaneously, which makes the model more versatile in complex fields that require the integration of different data types.
- Extended Context Windows: Extended context windows are important when keeping long conversations or complex tasks flowing. But big context capacities pose risks: it could be used in “multi-shot jailbreaking” through iterative prompts, the intended use of the model might yield harmful or unintended outputs.
- Efficient Edge Deployment: With frontier AI models like LLaMA 3.2, edge computing can be applied to devices such as smartphones or other mobile systems, which allows quicker processing while preserving user privacy through local data.
- Tool and API Integration: Models like Claude 3.5 are being developed to interact with tools and APIs, enabling them to perform digital actions such as navigating websites or filling out forms. This opens doors for automation in various professional settings.
- Generalization Across Tasks: Frontier models are designed to perform a variety of tasks without the need for specific, task-based training. This flexibility makes them ideal for use in industries like healthcare and finance, where models must handle dynamic data and diverse tasks.
Use Cases of Frontier AI Models
- Customer Support Automation: Models with extended context and multimodal capabilities offer personalized responses and solutions, streamlining customer service operations.
- Healthcare Diagnostics. While applying the multimodal models in the healthcare industry, analysis of data through patients and medical imagery is allowed, thereby speed up diagnostics.
- Education: Frontier AI models allow for tailored learning paths, testing students’ performance and fine-tuning content to student’s learning speed and individual preference.
- Real-Time Mobile Applications: Real-time image processing can be applied to edge-optimized models for mobile devices, making the applications range from augmented reality to retail.
- Legal Document Review: Models with high windows like Gemini can process legal documents speedily where lawyers and analysts realize complex cases faster.
Seamless Use of Frontier AI Models on Agentic AI
- Tailored AI Agent Deployment: Agentic AI allows businesses to create and deploy intelligent agents customized for specific tasks like automation, data analysis, and prediction. This ensures that AI solutions align precisely with unique business needs.
- Effortless Integration of Cutting-Edge AI Models: The platform simplifies incorporating advanced AI models into workflows for tasks such as text generation, image analysis, and predictions. Businesses can adopt these models easily without requiring extensive technical expertise.
- Multi-Modal Input Support: Agentic AI supports inputs like text, images, and audio, ensuring flexibility and compatibility for diverse applications. This capability enables businesses to address multiple challenges with a unified solution.
- API Integration for Workflow Automation and Scalability: Robust API support enables businesses to automate workflows and integrate AI agents into existing systems. This ensures scalable solutions that grow with organizational needs.
- Comprehensive Documentation and Support: Extensive documentation and support empower users to fine-tune AI agents for optimal performance. This ensures efficient and effective AI deployment for real-world applications.
Challenges Facing Frontier AI Models
While these models are groundbreaking, they come with few challenges:
- Ethical Issues and Bias: Frontier AI models are prone to biased or inappropriate output, especially when the content is controversial, slanted, or simply ignorant. To eliminate such biases, pursuing an ethical deployment of AI is crucial.
- Data Protection and Security: Handling large, sensitive datasets increases the risk of privacy breaches. Edge deployments like LLaMA 3.2 help, but ensuring data security remains a priority, especially in sectors like healthcare.
- Resource-Intensive Deployment: Training these models can be very computer-intensive and, therefore increased costs to deploy them. This limits their accessibility and may thus prove difficult for smaller organizations to integrate such models.
- Multi-Shot Jailbreaking Risks: Extended context windows are prone to “multi-shot jailbreaking” Here, a series of prompts exploit the memory of the model in order to circumvent safety mechanisms and create harmful content. For these, moderation and alignment methods need to be fine-tuned for safe interactions.
- Alignment to Human Values: Then, it raises a tough question of whether such models would respect human values and give ethical answers since there is a possibility that models may unknowingly take harmful biases. More value alignment research is required to develop AI responsibly.
The Role of Regulation in Frontier AI
As frontier models advance, there is a compelling need for regulatory frameworks to address the risks that it could potentially pose. Regulators, AI developers, and other stakeholders are focusing on establishing safety protocols, transparency, and accountability when dealing with such models.
Major Regulatory Approach
- Testing and Red-Teaming: Testing and red-teaming, where the experts try to “break” the model, constitute proactive safety measures in this kind of scenario. These kinds of tests are necessary for models that have huge context windows to avoid its misuse.
- Transparency Standards: It has also been suggested that developers need to shed light on their training procedures and data sources. This promotes stakeholder trust and discussion regarding the limits and potential bias of such models.
- Hazard assessment procedures: A frontier model should undergo thorough systematic risk analysis so as to evaluate the impact it has on society. The models applied in very sensitive applications such as healthcare have to be tested aggressively by stringent safety standards.
- Clear Usage Guidelines: Developers should set usage policies that allow users to use these models responsibly. In fact, such clarity empowers companies to reduce misuse while also encouraging useful applications.
- Data Protection: Privacy-focused regulations are essential, especially for models handling sensitive data. Guidelines are being developed to protect personal information, particularly for models deployed on edge devices like LLaMA 3.2, where local data processing can enhance privacy protections.
Conclusion: Frontier AI Models
Frontier AI models are transforming the Agentic AI landscape by extending their capabilities beyond traditional limits, enabling them to function across diverse domains and adapt to a wide array of tasks. This adaptability allows organizations to utilize these models for innovative applications that were previously unimaginable, driving efficiency and enhancing decision-making processes.
To responsibly harness the benefits of these models, effective regulation is paramount. Ongoing innovation in safety, alignment, and transparency must be prioritized to mitigate risks associated with these advanced technologies. By establishing robust frameworks for oversight and promoting best practices in development and deployment, stakeholders can ensure that frontier AI contributes positively to society while minimizing potential harms.