Introduction to Intelligent Process Automation
Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) has become a buzzword. Where the speculators have perspectives ranging from “farfetched” and “too good to be true”. To anticipate that the future of Automation is unfolding right in front of us. The hype created around the subject clearly explains the need for organizations to adopt it. But the subject is off the radar for some business organizations mainly due to a lack of technological expertise or simply because they’re too busy to learn more.
IPA is that side of Automation, which will help it significantly shift technology. Automation contributes by developing and exploiting new intelligence types to make seemingly space-age innovations available today, from driverless cars to autonomous drones. Whether it is customer correspondence in mobile assistants or an enterprise-wide automated job. Automation changes the way we live and function. Companies need to orchestrate their complex operations through automated processes to deliver services based on that Automation.
What is Intelligent Process Automation?
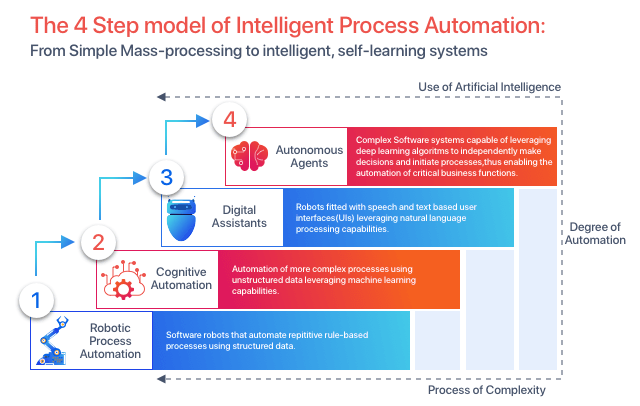
Intelligent Process Automation applies AI and related new technologies, likewise cognitive Automation, computer vision, and machine learning, to Robotic Process Automation. It is a blend of the most advanced technologies used to manage and automate digital processes. It is used as an “assistant to humans” who performs all the manual, repetitive and routine tasks that were previously being performed by their counterparts. This crossroads of emerging technologies produces automation capabilities that drastically improve the business value and give a competitive advantage to the organization. With these technologies — especially with AI and machine learning — an IPA tool should learn how to change and enhance the process flow to construct an intelligent procedure. With time it should be able to learn and develop. IPA is essential in automating more and larger portions of enterprise employment. IPA enables users to more rapidly and easily scale up their automation use cases and carry out more complex tasks, such as automatically detecting objects on a screen or using technologies like Natural Language Processing (NLP).
What are the Business Drivers of IPA?
- Customers: use contextual knowledge to gain insights into consumer behaviors and expectations.
- Cybersecurity: to ingest and grasp large network data flows and to make automated decisions to identify cyber threats.
- Modernization: Integration of digital development programs and processes.
- Efficiency: Cost savings due to fiscal constraints and productivity targets.
- Speed/agility: meeting rising demands of customers for speed of service and new capabilities.
- Quality: Strengthening standardization to ensure clear organization compliance.
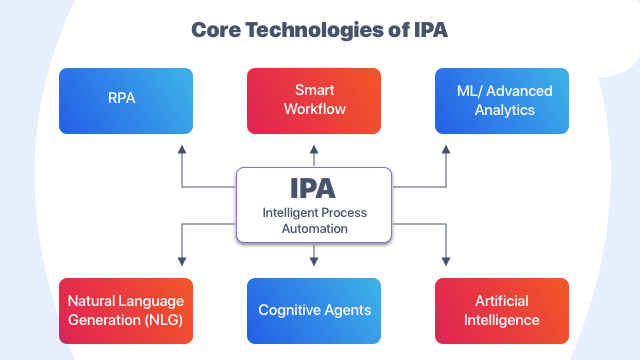
What are the Core Technologies involved in IPA?
Intelligent Process Automation in its full extent encompasses five core technologies:
Robotic Process Automation: A software automation tool that automates regular tasks. Such as data cleaning and extraction through existing user interfaces. The robot has its own user ID just like a person and can perform defined tasks such as accessing email and systems, creating documents, performing calculations and reports, and checking files. RPA helped one major insurance company eliminate excess queue procedures impacting 2,500 high-risk accounts every day, freeing up 81% of FTEs to take on constructive account-management roles instead.
Smart Workflow: A process-management software tool that combines tasks performed by human and computer groups (for example, sitting on top of the RPA to help control the process). This enables users to initiate and monitor the status of an end-to-end process in real-time; the program will handle transfers between various classes, including between robots and human users, and will provide statistical information on bottlenecks.
Machine Learning / Advanced Analytics: Algorithms that identify structured data patterns, such as daily performance data, through “supervised” and “unsupervised” learnings. Supervised algorithms learn from structured data sets of inputs and outputs before making predictions based on new inputs on their own. Unsupervised algorithms monitor structured data and begin to provide insights on recognized patterns. For example, in the race to strengthen enforcement, minimize cost structures, and gain a competitive edge. From new insights, Machine Learning and advanced analytics could be a game-changer for insurers. Advanced analytics have already been widely applied in leading HR groups. To recognize and analyze key characteristics in leaders and managers to help predict behaviors, build career paths, and plan leadership succession.
Natural-Language Generation: Computer engines build seamless human-technology interactions by following rules to translate data observations into prose. Broadcasters were using natural language technology to write stories about games in real-time. Structured output data can be piped into a natural-language engine to write internal and external management reports automatically. A significant financial institution has used the NLG to reproduce its weekly stats.
Cognitive Agents: Technologies that combine NLG (Natural Language Generation) and machine learning to create a completely automated workforce (or “agent”) capable of performing tasks, interacting, learning from data sets, and even making “emotion detection “- based decisions. Cognitive agents may be used, for example, in employee service centers. To help employees and customers over the phone or via chat. A UK auto insurer using cognitive technology reported a 22 percent rise in conversion rates. A 40 percent reduction in validation errors, and an average return on investment of 330 percent.
Artificial Intelligence: Artificial intelligence is illustrated by machines, in contrast to humans’ natural intelligence (NI).
What are the differences between RPA vs IPA?
Intelligent process automation and Automation of robotic processes are related processes; however, IPA covers a greater work scope than RPA. In general, RPA is intended to be used for specified processes based on the rules. In addition, IPA is used for more complicated operations, which can benefit from the use of AI, machine learning, NLP, predictive analytics, and other technologies like RPA. IPA can also handle more data formats and require more smart decision-making forms. Both IPA and RPA are useful and have cases of their own best use. However, IPA requires RPA to be formed first. A successful IPA approach needs more in-depth coordination between IT and data science teams than RPA
Use Cases of Intelligent Process Automation
Since IPA and RPA are similar, they can expand the environment with IPA as soon as an entity has a stable RPA environment — using the preceding environment as a foundation. Using IPA, companies can replace manual and repetitive tasks beforehand, interpret text with NLP. Makes computer-based decisions with machine learning, monitor systems and individuals, and give consumers recommendations using cognitive agents. There’s been more of a case to be made in the past about whether a company should use IPA or RPA. But now, it’s agreed that companies can use IPA to spread a broader strategy around RPA. Rather than getting all the IPA-related technologies implemented separately, an IPA platform will bind them together to create more agile and efficient business operations. Insurance, banking, and general-enterprise companies may use an IPA tool. An IPA tool will interpret the required text, decide how to share the data, and give customer feedback based on their input.
Market Outlook and Leading Tools
According to Deloitte’s 2019 global robotics report, executives prediction. That smart Automation will produce a 22 percent average cost reduction and an 11 percent rise in sales over the next few years. IPA is becoming more popular as more and more popular vendors start selling more IPA products and automation tools for the workflow. Many IPA, or Smart RPA products, include:
- Another Monday, offering an automation platform capable of automatically recording process logic, pulling tasks from a database, and delivering a drag-and-drop user interface.
- UiPath, a well-known RPA application that supports IPA functionality, too. This method is ideal for automating any mobile or web device.
- Anywhere, Automation is another RPA method that has started adopting IPA qualities. It can combine RPA with technologies like understanding the language and reading unstructured data.
What are the Benefits of Intelligent Process Automation?
“Several businesses across sectors have experimented with IPA, with remarkable results: 50 – 70 percent automation of operations, which has translated into 20 – 35 percent annual run-rate cost efficiencies,” McKinsey reports. This is achieved in the following ways:
- Orchestration of humans and robots: Instead of merely deploying technologies such as RPA in silos and leaving them to complete individual tasks. IPA can help organize work among robots, people, and systems. All robotics are well and well, but when you combine them with an IPA platform, you’re going to end up with isolated solutions as opposed to business-wide solutions.
- Freeing up employees from routine tasks: Employees may be released by RPA from labor-intensive tasks and put to work in more efficient areas. By partnering with DPA and AI, you can be assured. The right decision will be made, as it is designed in AI to help make informed decisions along the way.
- Ensuring proper governance and minimizing risk: RPA can release employees from labor-intensive tasks and put them to work in areas of greater efficiency. By collaborating with DPA and AI, you can be confident that the right decision will be made. As it is built to aid informed decision making along the way in the AI process.
- End-to-end visibility of Processes: When the individual automation technologies are deployed, the enterprise-wide result can be challenging to see. You can see the entire process using IPA, helping you find bottlenecks or points. At which customer travel might be smoother.
- Agility and speed of process change: IPA allows you to accelerate end-to-end delivery and encourages agile development and enabling technology improvements. That helps organizations develop their business processes continuously.
What are the Challenges and Opportunities?
Focusing on process automation is a significant opportunity to improve processes, reduce operational costs and become more receptive to clients. Although the prospects are substantial, the endeavor is not without challenges.
Challenges of Intelligent Process Automation
- There are high expectations for labor-centric Automation, particularly when the IA solutions combine RPA and capture software. As crucial as IPA is, using it on its own is unlikely. To deliver the full benefits that a broader portfolio of process enhancement technologies can achieve. Integration and workflow will continue to play a vital role in optimizing processes.
- Continuing innovation, especially new design patterns, is available due to technological changes.
- Develop machine learning skills to help predictive and prescriptive analytics. That can dramatically change complex actions or processes and enhance decision-making.
Opportunities Intelligent Process Automation
- Building more integrated capacity within the enterprise to simplify and automate processes with a specific and forward-looking perspective on how a cross-section of technology can support and be used for innovation
- Build a community for everyone. They are empowered to learn more about simplifying and automating. Wherever it makes sense by sharing achievements and implementing software tools that allow users to self-train and automate when they see opportunities.
- Detect process improvement areas that will benefit from using predictive analytics. To detect challenges and prescriptive analytics to assess the next steps and workflow to execute the decisions.
Conclusion
With the ever-increasing competition in mind, demand for advanced work automation tools has increased, and in the coming years, it is expected to rise multiply. Moving beyond traditional business process management boundaries. Intelligent process automation software is designed to assist processes in more than managing operations. Right from identifying and removing the performance bottlenecks. The smart process automation software deploys advanced analytics. That helps analyze overall performance, understand the ever-changing market dynamics, and formulating strategies accordingly. To the ever-changing demands of tech-savvy customers.