Introduction to Edge AI
Edge AI, as the name suggests, is AI models working on Edge or on-site. When deploying ML models, there is no need to send API requests or real-time data to cloud servers for each inference. With the rise of Edge computing and supporting devices, a new marketplace has opened up for Artificial Intelligence applications. Now, Machine Learning Models can be deployed locally without the need for internet connectivity. Models deployed on Edge devices are capable of real-time data collection and inference on the spot.
ML models stored on Edge can be updated or maintained through regular connectivity with cloud platforms or with their neighboring Edge nodes. Well-established Edge device providers also provide cloud platforms to build/train, deploy, and monitor the models in case troubleshooting and upgrading are needed.
Edge AI architecture usually involves:
- Cloud Platform: A managing cloud platform provides regular software and model maintenance by regular checks. Metrics and scores of the model are transmitted to the cloud servers regularly, and data transmission, too, in case there is a need for re-training the model. The desired changes are then sent to the edge devices.
- Edge devices: Deployed locally to the location where they collect data and perform real-time analysis. They usually work offline but connect to cloud servers at regular intervals for software and model checks and updates.
- Environment: The environment is fitted with edge devices, which provide sensor readings, video streams, or any input data configured in the edge devices. The operators at the locations receive the inference of edge models and use them for their work.
Benefits of Edge AI
AI algorithms can understand applications of Edge computing and forms similar to speech, sights, sounds, smells, temperatures, faces, and other unstructured information, making them particularly useful where end users are engaged with real-world problems. However, due to latency, bandwidth, and privacy concerns, these AI applications are impractical or impossible to deploy in centralized clouds or enterprise data centres.
The benefits of edge AI include:
Intelligence
AI applications are more powerful and flexible than traditional applications, which can only respond to the inputs programmers expect. In contrast, AI neural networks are not taught to answer specific questions but to answer specific types of questions, even if the questions themselves are new. Without AI, it would be impossible for an application to process infinitely different inputs such as text, spoken word, and video.
Real-time Insights
Edge technologies respond to user needs in real time by analyzing data locally rather than in distant clouds, where long-distance communication introduces latency.
Reduced costs: By moving computing power closer to the edge, applications require less internet bandwidth, dramatically reducing network costs.
Better Privacy
AI can analyze real-world information without making it available to humans, greatly increasing the privacy of those who need to analyze their appearance, voice, medical images, or other personal information. Edge AI further improves data protection by storing this data locally and uploading only the analysis and insights to the cloud. Some data is uploaded for training purposes and may be anonymized to protect your identity. Edge AI simplifies your data compliance challenges by protecting your privacy.
High Availability
Decentralization and offline capabilities make Edge AI more robust as it does not require internet access to process data. This improves the availability and reliability of mission-critical, production-grade AI applications. Permanent improvements: AI models get more accurate the more data they train on. When an edge AI application is presented with data that it cannot process accurately or reliably, it typically uploads that data so the AI can retrain and learn from it. Therefore, the longer a model is in production on edge, the more accurate it will be.
How Edge AI Architecture Works?
In the early days of computing, applications and software were distributed physically via storage devices. This distribution mode was inconvenient because of the cost of hardware carrying the applications, the inaccessibility of the physical copy to some people, physical re-purchase for upgrade and maintenance of the applications, etc.
This problem was solved in the mid-2000s with the commercialization of cloud computing. Clouds made the management and distribution of applications cheaper and more efficient. It also opened a marketplace for smaller developers to share their applications and collaborate. Whether data storage or machine learning models, the cloud provides a comprehensive infrastructure to share resources and collaborate globally.
In the past 10 years, applications of cloud computing have grown exponentially. However, a new computing model has emerged to cater to problems like low latency and data security, which often come with using cloud technology. This model is known as Edge Computing.
Why is Edge AI Required?
Often, models are deployed in remote locations with little to no internet connectivity. In such cases, getting inferences from the models becomes impossible if they are deployed on the cloud. If the data required for inference is large, uploading the data to the cloud and waiting for inference becomes cumbersome and slow.
A nuclear plant located in a remote location would require regular sensor data monitoring to check for anomalies or radiation leakage. In such a situation, using Edge architecture would serve better than the cloud as it provides instant inference, and there is no need to upload the sensor data to the cloud each second.
Edge AI Devices
Commonly known devices used for Edge AI and Computing:
- Raspberry pi
- Lenovo ThinkEdge
- Advantech IPC-200
- Google Coral boards
- Jetson Series (NVIDIA)
Architecture: Most edge devices like Raspberry Pi have a 64-bit processor and RAM. Since edge devices are meant to be lightweight in processing, the memory comprises 1-4GB RAM. Still, some edge devices can upgrade RAM to higher memory to accommodate models that require high face detection model processing power. There are slots for SD-card storage and HDMI ports for input and output. Edge devices also come with a port for power supply and ethernet connectivity.
It is essential to mention that input and output devices, such as cameras or display screens, are designed to work with edge devices. For example, Pi Camera is designed to work with Raspberry Pi to capture high-definition images and videos.
Edge AI Platforms
Well-known platforms for Edge AI and computing:
- AWS Greengrass: AWS Greengrass is an open-source platform for managing IoT edge devices. It provides services for building, deploying, and managing edge device models. The Greengrass software is deployed on edge devices connected to Greengrass cloud services for support.
- Azure IoT Edge: Azure’s IoT Edge service provides a cloud platform for managing edge devices and using Azure’s services and packages on them.
- Google Distributed Cloud Edge: Google’s distributed cloud edge provides Google cloud services on edge devices. It is fully managed by Google, which also provides hardware solutions. It offers real-time data analytics with Google AI and analytics.
Applications of Edge AI in the Industry
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a system of interconnected devices working on Edge architecture. Apple Inc.’s Siri is an AI voice assistance application that does not need internet connectivity to operate. Similarly, many computer vision applications are gradually moving towards Edge architecture to deploy their models.
NVIDIA Metropolis is an application framework for creating and deploying Edge automation and AI applications to increase the efficiency of metropolitical institutions like airports, factories, farms, hospitals, etc. Arizona’s Maricopa County Department of Transportation (MCDOT) has used NoTraffic, an NVIDIA Metropolis partner, to reduce traffic on roadways in Arizona by using deep neural networks and computer vision to track real-time traffic flow.
Some sectors in which Edge AI is applied:
- Computer Vision: Surveillance systems utilize Edge AI for object detection, face recognition, and tracking to identify anomalous behavior, unauthorized access to systems or areas, identifying subjects with past criminal records, etc., to safeguard the organization and locality. Instant detection and recognition can aid security personnel in taking immediate action and stopping the malicious attack before it can cause further damage.
- Manufacturing: Data streams from manufacturing machines can be used for real-time analysis using Edge AI models to monitor the manufacturing process, control temperature/pressure conditions, optimize raw materials, etc. AI models can predict faults in the machinery by continuous analysis of the sensor data stream, which can lead to timely maintenance and calibration of the machinery, thus increasing productivity and reducing damage control requirements.
- Self-driving cars: To work properly, constant sensor data input and frequent analysis of the input data at millisecond frequency are needed. Edge AI provides the best infrastructure for instant inference of the sensor data to guide the car’s controls. Since the architecture is self-reliant, low bandwidth will not cause any problems.
How Edge AI Helps in Enhancing Security
As highlighted in this article, edge AI embodies a revolutionary enabler of change in security across sectors by incorporating AI with local data processing features. Here are some key ways in which Edge AI contributes to improved security measures:
Real-Time Threat Detection
- This will allow immediate analysis of data on objects such as surveillance cameras to perform their intended functions.
- Identifies and prevents suspicious behaviour in real-time and does not have to send collected data to some cloud centre.
Reduced Bandwidth Usage
- Performs data computations and operations locally and retransmits only necessary data to the cloud as and when needed.
- It sends only important notifications and usage reports instead of streaming raw data feeds and consumes much less bandwidth, thus improving overall system performance.
Enhanced Privacy and Compliance
- Data processing locally minimizes the exposure risks of transmitted data, as most of the data is processed within the locality.
- It suits industries with specific data privacy regulations concerning the data they input into their databases (e.g., the health sector or the finance sector).
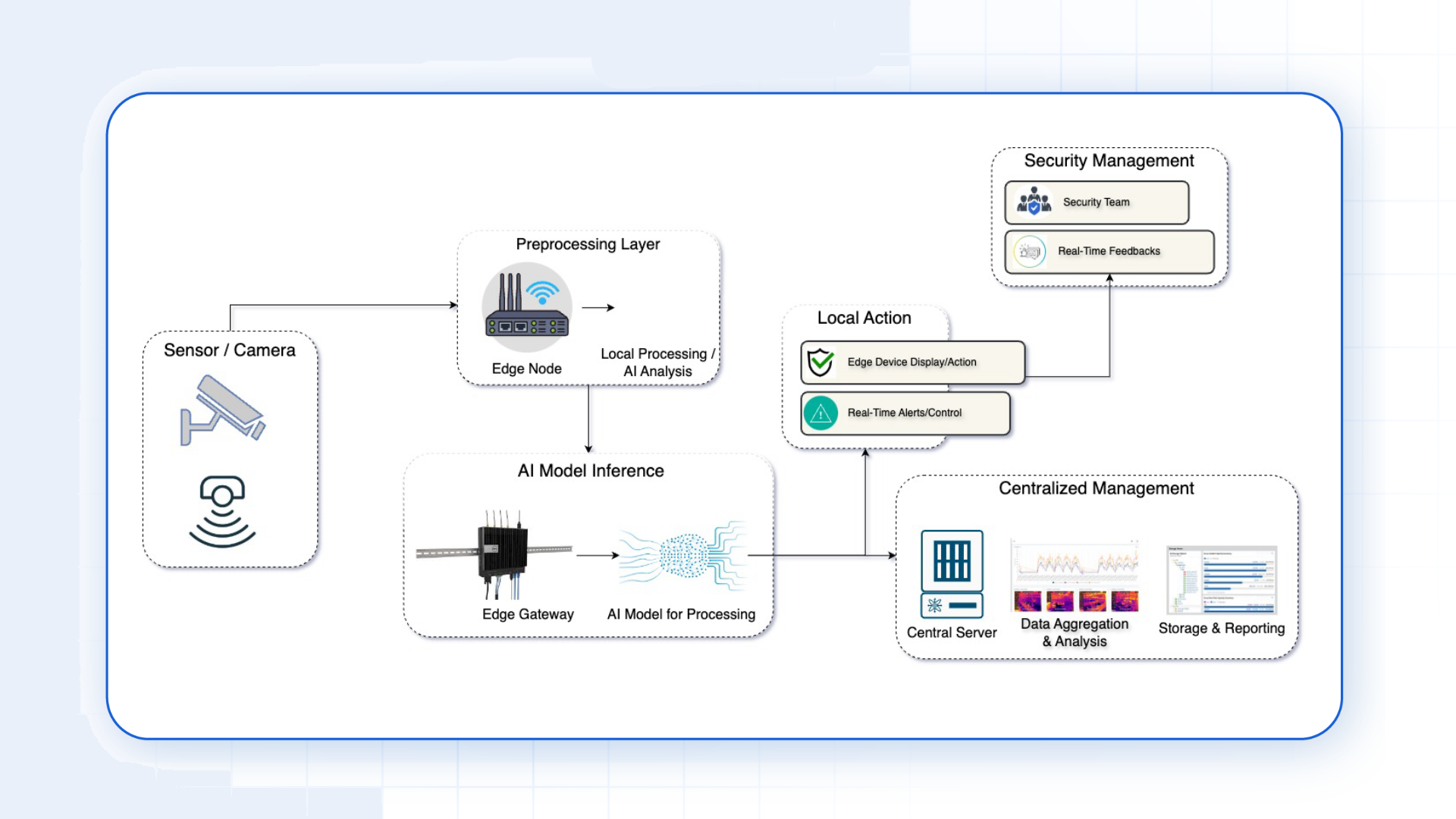
Robustness Against Cyber Attacks
- It disseminates intelligence across multiple platforms, thus avoiding the reliance on a single and centralized system, which is very vulnerable to hacking and other malicious programs.
- Uses isolated security strategies, for example, anomaly detection at various stages to discover extraordinary activities.
Operational Efficiency and Automation
- Offloads repetitive security tasks (watching, reporting) to technologies to eliminate the human factor in security operations.
- Self-service access control may be performed through autonomous AI systems where exceptional cases are forwarded to the next level.
Scalability and Flexibility
- Elaborate as the coverage areas and the number of devices added to the system can be increased without changing the system.
- Therefore, dynamic security requirements and transitions in artificial intelligence technology are suitable for evolving organizations.
Conclusion
Edge AI is fairly new in computation but has grown exponentially. Each year, we see new applications and technologies developing around them. Edge AI architecture benefits manufacturing, surveillance, and monitoring industries. With instant inference deliverance, little to no internet connectivity need, data security, privacy, and cost efficiency, Edge AI has the potential to revolutionize how AI technology is developed and used worldwide. With its convenient architecture, Edge technology can help AI implementation grow and be used more widely by the masses and institutions.