Introduction to Edge Computing
MEC (multi-access edge computing) integrates cloud computing capabilities and an IT service environment at the network’s edge to reduce latency. We live in a world where more than 85% of companies use cloud services, as suggested by the tech jury. According to we are social, 4.57 billion people are using the Internet, and this number is increasing. Consequently, there is a generation of a huge amount of computational and networking information, which overloads the central cloud. This is where Multi-Access Edge Computing comes into play. What led to such an advancement? Let’s discuss this. Cloud computing is used to analyze, process, and store data, rather than a local server or personal computer, without direct active management by the user. In other words, it is a system that allows the user to use the computer system resources only when required, with the basic requirement of a strong internet connection. The next level of cloud computing is “Edge Computing.” It reduces network stress. The basic difference between Edge and Cloud Computing lies in the place where data processing takes place.
What is Multi-Access Edge Computing?
It enables data to be processed, analyzed and transferred at the network’s edge. The idea is to offload the analyzed data from the centralized cloud to the edge of the network, closer to the user than the centralized cloud, far away from the user. Hence lowering the latency. Most modern devices, applications, and services make substantial use of cloud computing resources.
Cloud infrastructure is composed of various components that are interconnected with one another into a single architecture. It primarily composes hardware (CPU’s, GPU’s, RAM), virtualization, non-volatile storage, and network interface. But there is much more to computing, especially networks that decide how networked resources can be utilized. The main aspects that affect cloud computing services are latency and bandwidth. Cloud service latency is the delay between a client request and a cloud service provider’s response, and bandwidth in data transmission in bits per second represents the network connection’s capacity. MEC removes these two major drawbacks (high latency and low bandwidth).
Features of Multi-Access Edge Computing
Go through the main features of Multi-Access Edge Computing below:
- MEC offers IT services and cloud at the edge of a network and is truly an ace up your sleeves in situations where milliseconds play a crucial role.
- It brings the best of both worlds, combining the public cloud’s agility with the high responsiveness of on-premise.
- MEC reduces network congestion and accelerates an application’s performance, bringing high-quality graphics, VR (Virtual Reality), gaming, and more to IoT platforms and mobile devices.
Key Values of Multi-Access Edge Computing
Below mentioned are certain values related to Multi-Access Edge Computing that provide big advancements in handling the data:
- The advancement in it provides opportunities to develop a new range of services and applications using IoT, artificial intelligence, or 5G technology, hence helping in developing new revenue streams.
- The data produced at the user end is filtered at the edge and reduces the cloud data storage.
- Data processing takes place at the edge of the network, and this processed data is easily accessible by the user end. Hence, improve availability and reduce the data transportation cost. Edge Computing and its Impact on IoT
- Instead of sending unprocessed data to the cloud, most of the processing is done at the local network’s edge. Only the result is sent to the cloud, thus requiring low transmission bandwidth.
- It provides low latency, which in turn, increases the system’s efficiency.
What are the key drivers of Multi-Access Edge Computing?
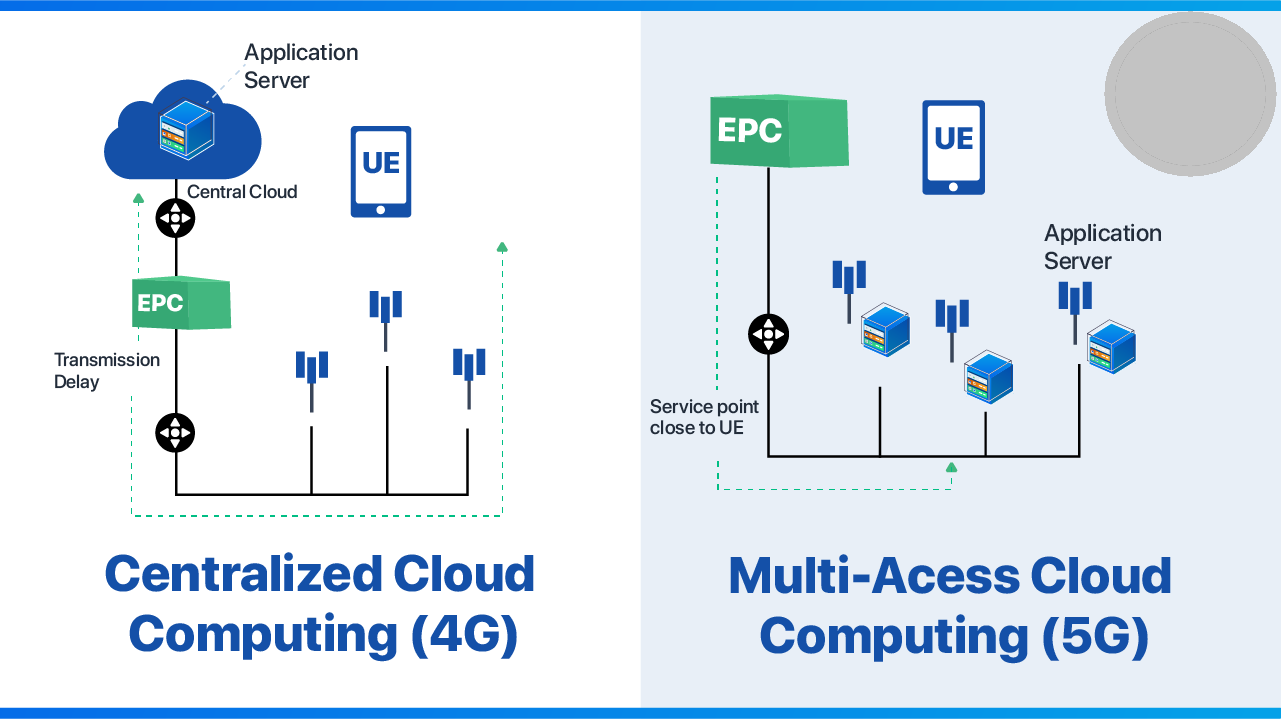
MEC’s key drivers are 5G networks, the Internet of Things (IoT), and 4G networks. Experts believe that it will become popular when 5G goes into the mainstream a year from now. 5G technology plays a significant role in improving the performance of applications and services. Mobile Edge Computing provides an ultra-low latency rate by bringing the computing capabilities closer to the user end, thus decreasing the distance traveled by the data. The user will be able to enjoy consistent connectivity.
IoT is a system enabling the interconnection of computing devices or physical devices and transferring data over the network without direct human interaction. The time taken to transfer the data must be below that is low latency, and the system must be secure, which can be provided by it. For example, if a Life Critical system collapses, it results in a life-threatening situation. We cannot afford the delay in response time. In these types of applications, we need a response time of fewer than 20 milliseconds.
What are the benefits of Multi-Access Edge Computing?
So what can be the benefits of it in Data Management? Know ahead.
Enhanced Data Security: Stop migrating your data to the cloud for external processing. Now you can process your data locally, thereby eliminating the risk of theft or illegal access.
Ultra-Low Latency: Bring computing power adjacent to your wireless network’s edge to process data in NRT (near-real-time).
Better Connectivity and Coverage: MEC cellular connectivity provides a cost-effective way to enhance your existing private network through an intelligent allocation of data assets.
Use Cases of Multi-Access Edge Computing
Below pointed are certain use cases of Multi-access Edge Computing around:
Customer Services: With MEC enabling a wider range of customer services than ever before, businesses and enterprises in commercial sectors are beginning to utilize it to expand and improve their basic services and create the opportunity to bring in more revenue with newer services.
Augmented & Virtual Reality: Augmented reality (AR) and Virtual reality (VR) are two of the hottest trends currently taking entertainment by storm. The success of apps like Pokémon Go and virtual reality headsets to the vast majority of mainstream game consoles has seen the popularity of both AR and VR skyrocket. Only MEC technologies have the capability to take AR and VR to the next level.
Commercial Operations: Alongside the customer services side of things, it is currently being utilized for a wealth of commercial operations and enhancing and improving businesses and enterprises’ everyday running. From security and distribution to asset management and data routing, MEC has a role to play in all of them.
Industrial IoT: One of the biggest transformations brought about by the expansion of the Internet of Things has occurred in the industrial sectors. In fact, IoT devices and operations that fall within this category are often referred to as the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
Emergency Services: As with the industrial Internet of Things, when it comes to emergency services, access to real-time data and information, as well as a reliable means of communication, can be the difference between safely responding to a situation and the unfolding of a disastrous situation.
Conclusion
Multi-access edge computing technologies are widely revolutionizing cloud computing ways now! It is an emerging technology that lets operators host content and applications close to the network’s edge. It also brings new levels of performance and access to mobile, wireless, and wired networks. Cloud computing affects aspects like latency and bandwidth. These two factors can greatly impact what applications and services are reliable in a given or even viable network. But it is often mentioned in discussions on the infrastructure of 5G networks, specifically for handling the huge amounts of IoT devices (commercial and industrial) that are constantly connected to the network. Who would now not think of employing Multi-Access Edge Computing, above all, for managing cloud data?



